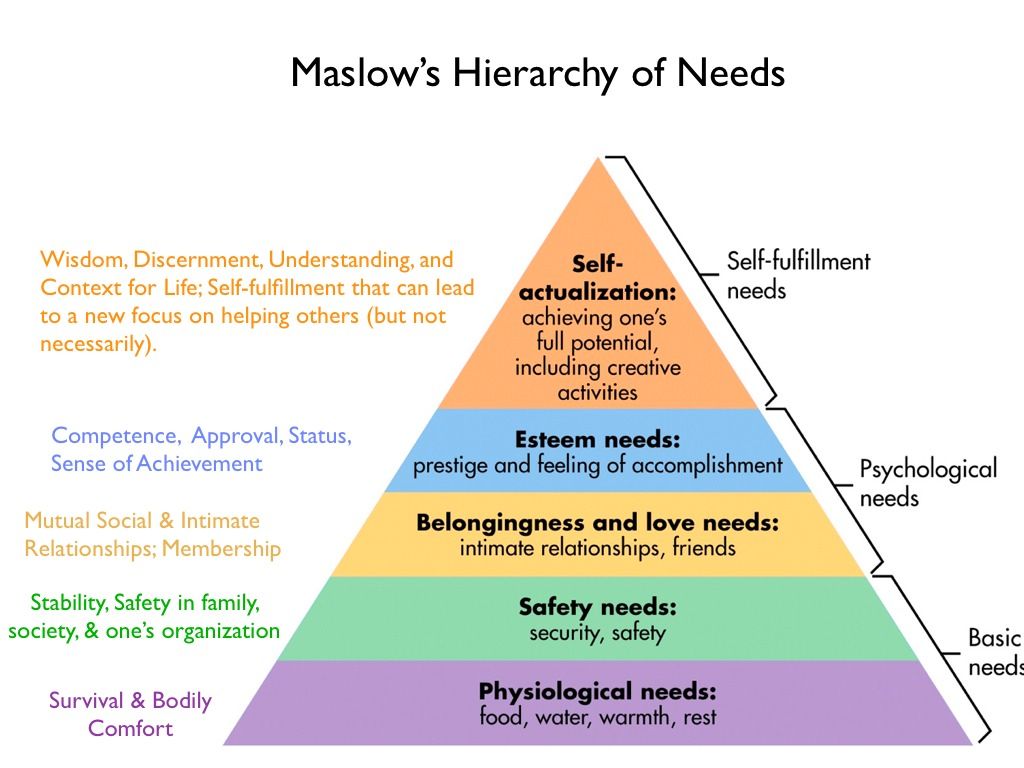
Maslow's Hierarchy of Need
Helping the world become smarter, happier and richer.
Physiological needs include:
(a) Air
(b) Water
(c) Food
(d) Heat
(e) Clothes
(f) Urination
(g) Excretion
(h) Shelter
(i) Sex and
(j) Sleep
Key Takeaways
(a) Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is a motivational theory in psychology comprising a five-tier model of human needs, often depicted as hierarchical levels within a pyramid.
(b) The five levels of the hierarchy are physiological, safety, love/belonging, esteem, and self-actualization.
(c) Lower-level basic needs like food, water, and safety must be met first before higher needs can be fulfilled.
(d) Few people are believed to reach the level of self-actualization, but we can all have moments of peak experiences.
(e) The order of the levels is not completely fixed. For some, esteem outweighs love, while others may self-actualize despite poverty. Our behaviors are usually motivated by multiple needs simultaneously.
(f) Applications include workplace motivation, education, counseling, and nursing.

Psychological needs
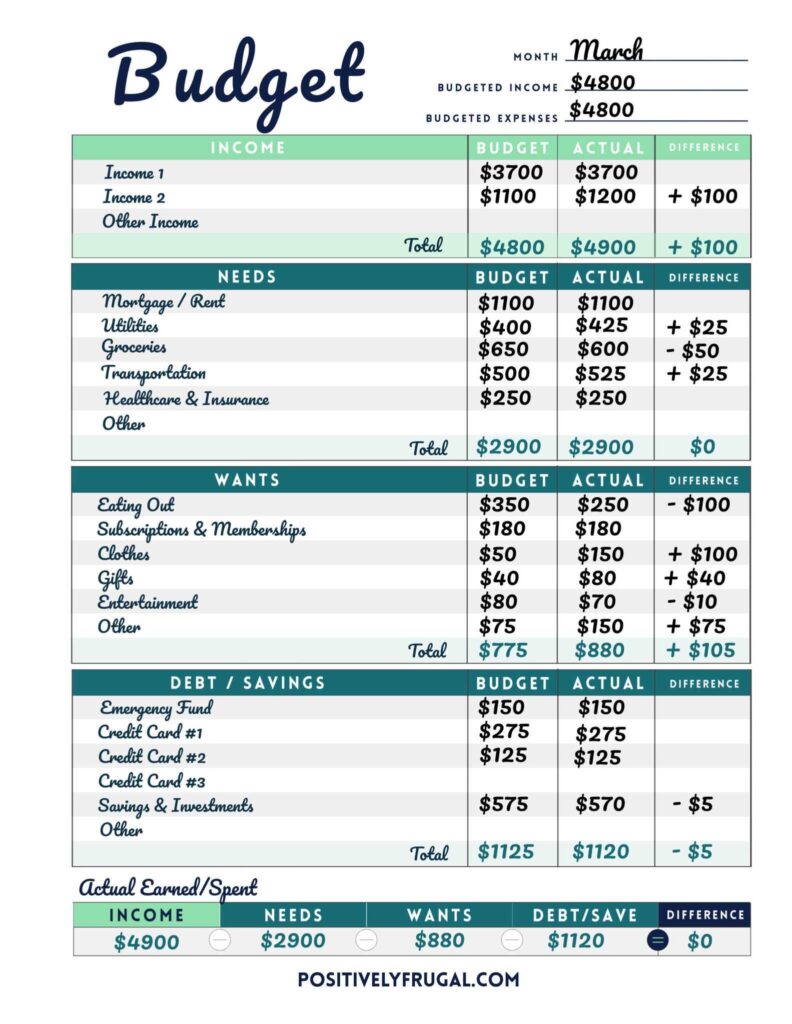
Why Is Budgeting So Important?
2. Budgeting Can Help with Retirement
3. Budgeting Can Help You Fix Bad Spending Habits
4. Budgeting Gives You Control of Your Finances
5. Budgeting Ensures You Only Spend What You Can Afford
6. Budgeting Can Improve Family Life
7. Budgeting Can Reduce Financial Stress and Improve Mental Health


How to Make a Budget: Your Step-by-Step Guide...
Why Budgeting Is Important?
How To Create a Successful Budget
Why Budgeting Is Important?
Contributed by: Amy Bell
Reviewed by: Pamela Rodriguez
Fact checked by: Suzanne Kvilhaug
Personal Finance/Financial Literacy
Budgets: Everything You Need To Know

Monthly budgeting is a common challenge. Whether you’re managing your family’s finances, running a business, tracking your personal spending, or planning for college, the costs can seem endless. Creating a monthly budget spreadsheet is a useful way to keep track of all these expenses and compare them with your income, so you can gain control over your finances.
Of course, there are many different ways you can budget money, depending on your income source, family size, and the level of visibility you want into your finances. You may also want to create separate budgets for special purposes, such as retirement, college savings, or home improvements, in addition to your personal monthly budget. Perhaps you’re interested in creating a budget for monthly business expenses or corporate projects. That’s why we created this comprehensive list of monthly budget templates. No matter what you’re budgeting for, this collection has a template to meet your needs...Read more
Personal Monthly Budget
Video:

Successful people tend to have a positive attitude and exhibit a number of traits and habits that help them achieve their goals:
Buy & Sell Online Businesses
Inflation:
What It Is And How To Control Inflation Rates
Useful links:
Mistakes:
Definition, Examples, & How To Learn From Them
The 10 Most Common Mistakes in Life (and How to Fix Them)
By: Electra Michaelidou,
Career and Lifestyle Writer
Reviewed by: Chris Leitch
Recovering from Life's Biggest Mistakes
Knowledge Sharing / Motivation

Ignoring good advice, believing it didn’t apply to me, because I was not yet ready to receive it – and wasting years of my life until I finally came around and understood how valuable that information was.
The Biggest Mistake I Made In My Life Is This...
I didn’t truly value my time or the opportunities it afforded me: I pretended I would get another chance, and so instead spent time on things that didn’t matter in the long run and that I did not have to do – missing out on the single chance I had.
Video: