EveningCrest is free to undertake any type of foreign direct investment (FDI) in Malaysia without any restriction and limitation. It is also free to receive an investment funds in the form of equity injections from the non-residents…
Financial Intermediaries – Depository
Company’s registered business activities
FDI’s promotional techniques consist of : (a) providing information to potential investors; (b) creating an attractive image of the country as a place to invest; and (c) providing services to prospective investors. However, promotion is only one of several tools available to countries eager to attract foreign investment.
World Bank Group – eLibrary
Governments can : (i) provide tax incentives and grants; (ii) provide industrial estates, export processing zones, and other infrastructure; (iii) attempt to simplify the bureaucratic procedures facing potential investors; (iv) negotiate bilateral tax, trade and investment treaties; and (v) attempt to create a favorable environment by guaranteeing repatriation of profits, assuring access to imported components, and promising not to expropriate property without compensation.
World Bank Group – eLibrary
EveningCrest is a registered company with the Bank Negara Malaysia (Central Bank of Malaysia) (hereinafter to be known as “BNM”) to receive Foreign Currency (Foreign Direct Investments/FDI) under the prevailing of Foreign Exchange Policy (FEP) with the registered BNM’s Reference Number: 21055643 / 21056012 / 21056435.
BNM highlighted that under the prevailing of foreign exchange policy (FEP) that:
- The company, EveningCrest is free to undertake any type of foreign direct investment (FDI) in Malaysia without any restriction;
- The company, EveningCrest is also free to receive an investment funds in the form of equity injections from the non-residents (investors, investment associates or business partners) and,
- If such inflow of foreign currency is in the form of lending to a resident entity (EveningCrest), the resident (EveningCrest) is free/allow to borrow in it from the non-residents (including a direct share participations) in:
- (a) Ringgit currency for any allowable sector activity in Malaysia.
- (b) Unlimited amount in the form of foreign currency.
Via BNM’s Confirmation Email: Tue, Apr 6, 2021.
Examples:
RECEIVER INFORMATION / BANKING COORDINATES:
Client Receiver Bank Name/Add.:
Client Receiver Company Name: EVENING CREST SDN BHD
Client Receiver Company Add.: C-03A-01, COLONIAL TOWER EMPIRE CITY DAMANSARA, DAMANSARA PERDANA, JALAN PJU 8, 47820 PETALING JAYA, SELANGOR, MALAYSIA.
Client Receiver Account Name: EVENING CREST SDN BHD
Client Receiver Account:
Client Receiver Bank Customer ID:
Client Receiver Swift Code:
Client Receiver Represented Passport Number, Issued & Exp. Date:
Client Receiver Bank Officer Name and Mail:
Client Receiver Bank Officer Email:
Client Receiver Signature Account:
Client Receiver Corporate Advisor:
fDi Intelligence is an English-language bi-monthly news and
foreign direct investment publication, providing an up-to-date
review of global investment activity.
Foreign direct investment (FDI) has been crucial in supporting developing economies to participate in global trade by facilitating the flow of capital, talents, and knowledge. To understand its transformational power, we measure FDI’s impact on economic growth in the Asia Pacific region, and discuss policies for maximizing its benefits. For evidence of FDI’s impact, we look no further than China in our infographic and a series of comprehensive papers.
Remarks:
Foreign direct investment (FDI) is a powerful instrument for growth and development, and is key to enhancing prosperity worldwide and boosting the global economy. Building on its previous work on the subject, the Global Agenda Council on Global Trade and FDI has been examining ways to encourage more FDI in both developed and developing countries. – By Davos World Economic Forum. See Video on FDI (WEF, Davos)
Foreign direct investment (FDI) has proved to be resilient during financial crises. For instance, in East Asian countries, such investment was remarkably stable during the global financial crises of 1997-98. In sharp contrast, other forms of private capital flows—portfolio equity and debt flows, and particularly short-term flows—were subject to large reversals during the same period (see Dadush, Dasgupta, and Ratha, 2000; and Lipsey, 2001). The resilience of FDI during financial crises was also evident during the Mexican crisis of 1994-95 and the Latin American debt crisis of the 1980s. – By IMF (Finance & Development)

How The Economic Machine Works by Bay Dalio
Retooling Global Foreign Direct Investment
Asian Economies by FDI (1990-2020)
Overview of the economy and how to attract Foreign Investment
Dr. M: We are still open to foreign investment
5th Eastern Economic Forum 2019 in Vladivostok, Russia
Malaysia’s 1Q 2022 performance on FDI
Foreign direct investment (FDI) is an investment from a party in one country into a business or corporation in another country with the intention of establishing a lasting interest. Lasting interest differentiates FDI from foreign portfolio investments, where investors passively hold securities from a foreign country. A foreign direct investment can be made by obtaining a lasting interest or by expanding one’s business into a foreign country. FDI is also defined as an ownership stake in a foreign company or project made by an investor, company, or government from another country. Generally, the term is used to describe a business decision to acquire a substantial stake in a foreign business or to buy it outright to expand operations to a new region. The term is usually not used to describe a stock investment in a foreign company alone. FDI is a key element in international economic integration because it creates stable and long-lasting links between economies.
Keynotes about FDI
- Foreign direct investments (FDIs) are substantial, lasting investments made by a company or government into a foreign concern.
- FDI investors typically take controlling positions in domestic firms or joint ventures and are actively involved in their management.
- The investment may involve acquiring a source of materials, expanding a company’s footprint, or developing a multinational presence.
- The top recipients of FDI over the past several years have been the United States and China.
- The U.S. and other Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) countries have been the top contributors to FDI beyond their borders.
Examples
In 2020, foreign direct investment tanked globally due to the COVID-19 pandemic, according to the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development. The total $859 billion global investment that year compared with $1.5 trillion the previous year. And China dislodged the U.S. in 2020 as the top draw for total investment, attracting $163 billion compared with investment in the U.S. of $134 billion. In 2021, global FDI bounced back by 88%.
In Malaysia foreign direct investment for 2021 was $18.60B, a 358.16% increase from 2020. Malaysia foreign direct investment for 2020 was $4.06B, a 55.67% decline from 2019. Malaysia foreign direct investment for 2019 was $9.15B, a 10.24% increase from 2018.
How Does Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Work?
Companies or governments considering a foreign direct investment (FDI) generally consider target firms or projects in open economies that offer a skilled workforce and above-average growth prospects for the investor. Light government regulation also tends to be prized. FDI frequently goes beyond mere capital investment. It may include the provision of management, technology, and equipment as well. A key feature of foreign direct investment is that it establishes effective control of the foreign business or at least substantial influence over its decision making.
The net amounts of money involved with FDI are substantial, with more than $1.8 trillion of foreign direct investments made in 2021. In that year, the United States was the top FDI destination worldwide, followed by China, Canada, Brazil, and India. In terms of FDI outflows, the U.S. was also the leader, followed by Germany, Japan, China, and the United Kingdom.
FDI inflows as a percentage of gross domestic product (GDP) is a good indicator of a nation’s appeal as a long-term investment destination. The Chinese economy is currently smaller than the U.S. economy in nominal terms, but FDI as a percentage of GDP was 1.7% for China as of 2020, compared with 1.0% for the U.S. For smaller, dynamic economies, FDI as a percentage of GDP is often significantly higher: e.g., 110% for the Cayman Islands, 109% for Hungary, and 34% for Hong Kong (also for 2020).
Special Considerations
Foreign direct investments can be made in a variety of ways, including opening a subsidiary or associate company in a foreign country, acquiring a controlling interest in an existing foreign company, or by means of a merger or joint venture with a foreign company.
The threshold for an FDI that establishes a controlling interest, per guidelines established by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), is a minimum 10% ownership stake in a foreign-based company. That definition is flexible. There are instances in which effective controlling interest in a firm can be established by acquiring less than 10% of the company’s voting shares.
Types of Foreign Direct Investment
Foreign direct investments are commonly categorized as horizontal, vertical, or conglomerate.
- With a horizontal FDI, a company establishes the same type of business operation in a foreign country as it operates in its home country. A U.S.-based cellphone provider buying a chain of phone stores in China is an example.
- In a vertical FDI, a business acquires a complementary business in another country. For example, a U.S. manufacturer might acquire an interest in a foreign company that supplies it with the raw materials it needs.
- In a conglomerate FDI, a company invests in a foreign business that is unrelated to its core business. Because the investing company has no prior experience in the foreign company’s area of expertise, this often takes the form of a joint venture.
Examples of Foreign Direct Investment
Foreign direct investments may involve mergers, acquisitions, or partnerships in retail, services, logistics, or manufacturing. They indicate a multinational strategy for company growth.
They also can run into regulatory concerns. For instance, in 2020, U.S. company Nvidia announced its planned acquisition of ARM, a U.K.-based chip designer. In August 2021, the U.K.’s competition watchdog announced an investigation into whether the $40 billion deal would reduce competition in industries reliant on semiconductor chips. The deal was called off in February 2022.
What is Meant by FDI?
Advantages and Disadvantages of FDI
FDI allows the transfer of technology—particularly in the form of new varieties of capital inputs—that cannot be achieved through financial investments or trade in goods and services. FDI can also promote competition in the domestic input market. As the name signifies, it is an investment scheme where any particular firm or any such individual makes an investment in one country (apart from their home country) into business interests located in another foreign country. Usually, FDI occurs when an investor sets up a foreign business operation, or they acquire a foreign business asset in any foreign company.
There are four main types of FDI, like the following:
- Horizontal FDI: The most well-known type is Horizontal FDI, which initially revolves around the investment of funds in a foreign company that belongs to the same industry and is either owned or operated by the FDI investor. In horizontal FDI, a company invests in a different company which is located in a foreign country, where both companies manufacture similar goods.
- Vertical FDI: Vertical FDI is another variety of foreign investments. A vertical FDI happens when a particular asset is made within a regular supply chain in a said company, which may or may not inevitably belong to the same industrial category. When a vertical FDI takes place, a business invests in a firm located that may provide or sell its products. Vertical FDIs can be further classified into two groups; such as forward vertical integrations and backward vertical integrations.
- Conglomerate FDI: When specific individuals or companies make investments in two entirely different companies belonging to completely different industries, the transaction is termed as a conglomerate FDI. As such, the FDI is not connected directly to the investor’s business or company.
- Platform FDI: The last type falling under foreign direct investment is called platform FDI. In the instance of a platform FDI, a business extends into a particular foreign country, but the commodities manufactured are exported to another different, third country.
Importance of FDI
FDI is integral to investment plans. The solution to foreign direct investment or FDI is the factor of control. Control depicts the intention of actively managing and influencing a foreign company’s operations, which is the primary differentiating determinant between passive foreign portfolio investment and an FDI.
Due to this reason, a 10% stake in the foreign company’s balloting stock is required to define FDI. But there are situations where this principle is not always implemented.
For instance, it is probable to exercise control over more broadly traded firms despite owning a lower percentage of voting assets.
Lists
- The Advantages of FDI
- The Disadvantages of FDI
- Comparison Table for the Advantages and Disadvantages of FDI
- FAQS on Pros and Cons of FDI
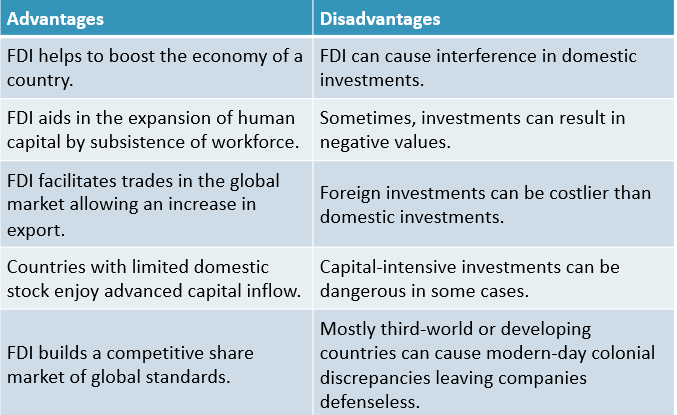
Advantages of FDI
- Boost in Economy: One of the major significant reasons a country (especially a developing nation) attracts foreign direct investment is due to the creation of jobs. FDI increases the production and services sector, which creates jobs and helps to decrease unemployment rates in the said country. Elevated employment explicates higher incomes and awards the population with added buying powers, advancing the overall economy.
- Human capital expansion: Human capital is concerned with the knowledge and subsistence of any workforce. Employees’ various skills gained through different training and practices can advance a particular country’s education system and human capital. Through a prolonged impact, it helps to train individual resources in other areas, trades and companies.
- Increased exports: Many assets produced by the FDI have global markets, and they are not solely based on domestic consumption. The production of 100% export-oriented segments helps to serve FDI investors in supporting exports from other foreign countries.
- Advanced Flow of Capital: The capital inflow is especially beneficial for countries with limited domestic resources and limited chances to raise stocks in the global capital market.
- Competitive Market: By promoting the entrance of foreign organizations into domestic markets, FDI advocates the creation of a competitive environment and breaks domestic trusts.
A solid competitive environment always shoulders firms to enhance their product contributions continuously, whereby promoting innovation. Consumers also earn access to a broader range of competitively valued products.
Disadvantages of FDI
- Impediment in domestic investment: At times, FDI can interfere with domestic investments. Due to FDI, countries’ local businesses begin losing interest in financing their household assets.
- Negatory exchange valuations: Foreign direct investments can seldom affect exchange rates to the benefit of one country and the disadvantage of another.
- More expensive costs: When investors invest in businesses in foreign counties, they may notice the increased expense than domestic exported goods. Frequently, more money is invested into motors and intellectual resources than in earnings for local workers.
- Financial non-viability: Acknowledging that foreign direct investments may be capital-intensive from the point of view of investors, they can at times be very dangerous or economically non-reliable.
- Modern commercial colonialism: Third-world with a history of colonialism is often troubled that foreign direct investment would end in modern economic colonialism, revealing host countries and leaving them defenseless to oppression by foreign companies.
FAQ’s on Pros and Cons of FDI
Question 1.
What are the directions for the transfer of shares against deferred payment in the case of FDI?
Answer:
In the case of transfer of shares among a non-resident seller and a resident buyer or vice-versa, not higher than twenty-five percent of the gross consideration can be met by the buyer on a deferred basis, within a term not surpassing eighteen months from the day of the transfer agreement. The amount deferred can also be each in the form of an indemnity or an Escrow. In any case, the price guidelines must be complied with.
Question 2.
On which does FDI depend?
Answer:
On the de-segregated level, FDI depends on the size and also growth potential of any national economy, tangible resources endowments and spirit of the workforce, openness to global trade and admittance to international markets, and state of physical, fiscal, and technological foundation.
Question 3.
Is FDI a practical option for developing countries?
Answer:
Both the commercial theory and recent experimental evidence suggest that FDI has a beneficial impact on developing host nations. Policy recommendations for such developing countries should improve the financing atmosphere for all kinds of capital, whether domestic or foreign.
Summary: Advantages and Disadvantages of FDI

Foreign Direct Investment in Vietnam
Understanding Foreign Direct Investment
It is the long term investment by a company in a foreign country.
Foreign Direct Investment – Dr. Justin Paul
Trade And Investments
ASEAN countries should engage in multilateral dialogue to resolve trade issues instead of adopting inward-looking protectionist measures, Malaysian Prime Minister Mahathir Mohamad said in his keynote address at the ASEAN Business and Investment Summit in Singapore, 2018.
ASEAN Trade in Goods Agreement
ASEAN Trade in Goods Agreement (ATIGA) aims to achieve free flow of goods in the region resulting to less trade barriers and deeper economic linkages among Member States, lower business costs, increased trade, and a larger market and economies of scale for businesses. Through ATIGA, Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand have eliminated intra-ASEAN import duties on 99.65 percent of their tariff lines. Cambodia, Lao PDR, Myanmar, and Viet Nam have reduced their import duties to 0-5 percent on 98.86 percent of their tariff lines. Today, focus is given to addressing non-tariff measures that could have non-tariff barrier effects on the region’s trade and business activities.
Protectionism and ASEAN’s Economic Community:
Ensuring Economic Security
Regional economic integration towards the ASEAN Economic Community has led to a more than five-fold increase in the size of regional GDP of ASEAN member states since they first set off on this path. This began with the ASEAN Free Trade Area in 1992, and the increase has been from approximately USD 500 Billion in 1995 to USD 2.7 Trillion by 2017 (in current US dollars). If these trends continue, it could allow for reducing regional poverty and potentially contribute to the global 2030 Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) of ‘ending poverty’.
Investment Statistics – MIDA – MIDA
Malaysia Foreign Direct Investment 1970-2023
Statistics of Foreign Direct Investment in Malaysia, 2021
Malaysia Foreign Direct Investment – 2022 Data – 2023 Forecast
Benefits and advantages of foreign direct investment
12 Foreign Direct Investment Advantages and Disadvantages
The benefits of foreign investment | Australian Government
Foreign Direct Investment Statistics: Data, Analysis and…
Foreign direct investment | Financial Times
Malaysia’s FDI: Major factors and the way forward
Foreign direct investments into Malaysia plunge
Malaysia Foreign Direct Investment – 2022 Data – 2023 Forecast -…
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) trends in Malaysia
Foreign direct investment – UNCTAD Handbook of Statistics 2022
Global foreign direct investment fell by 42% in 2020, outlook…
How the pandemic is impacting foreign direct investments | World…
FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT – The Economic Times
Foreign direct investment: it’s not all good | Financial Times
Foreign Direct Investment: Trends, Data Availability, Concepts…


