This examination is designed to test a candidate’s knowledge and understanding on the concepts
and rules and regulations pertaining to the compliance function. It is one of the examinations to
be passed by individuals who intend to hold the position of Head of Compliance or Compliance
Officer in a firm which is a holder of a Capital Markets Services License (CMSL) who carries on
the following regulated activities:
- dealing in securities;
- dealing in derivatives; or
- fund management in relation to portfolio management.
Candidates are advised to refer to the Licensing Handbook for the detailed combination of
examinations required for each regulated activity.
Candidates are expected to possess good knowledge and understanding of the subject matter
provided in this study outline and specified references. In addition, candidates are expected to
have relatively strong capabilities in the application and analysis of information in the module
and its references. It is estimated that this module will require a minimum of 120 hours of study
time.
Candidates may need less or more depending on the education background and work
experience.
Candidates are expected to update themselves with the latest changes relevant to this
examination as all questions will be continuously updated to reflect these changes.
Candidates
are permitted to refer to their own prescribed reference materials during the examination. Note
that no prescribed reference materials will be provided by the Securities Industry Development
Corporation (SIDC). The prescribed reference materials brought into the examinations by
candidates are subject to the terms and conditions of SIDC, details of which are set out in the
terms and conditions of the SC licensing examinations.
Candidates are required to comply with the terms and conditions of the SC licensing examination.
Severe penalties will be taken against candidates for any misconduct during the examination.
At the end of this study outline are 5 sample questions of various formats used in the Module 11
examination. The samples provided do not in any way reflect the level of difficulty or the subjectmatter distribution of the actual examination. They are merely intended to familiarise
candidates with the styles of multiple-choice questions used in the examination.
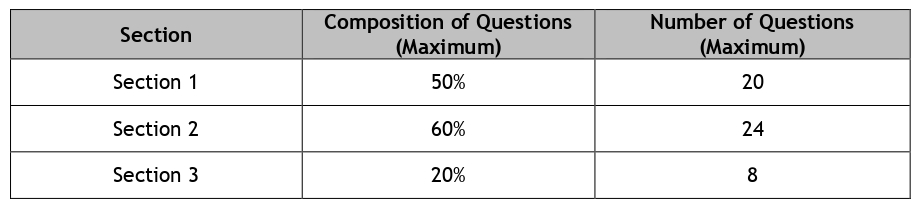
The syllabus for the examination is divided into 3 sections and the maximum composition of questions from each section is as follows:
Type of Questions: Multiple Choice
Number of Questions: 40 questions
Passing Mark: 70%
Time Allocated: 60 minutes
Details of the syllabus are as below:
Section 1/50%
Topic 1: Fundamentals of Compliance
1. The Concept of Compliance
2. Compliance and Control Functions
3. The Compliance Culture
4. Importance of Compliance
Topic 2: Roles and Responsibilities
1. Directors
2. Management
3. Internal Audit Department and Audit Committee
4. Risk Management and Risk Management Committee Mod
Topic 3: Compliance Officers
1. Compliance Officer
2. Role of the Compliance Officer in Relation to the Rules and Regulations of the Regulators
3. Role of the Compliance Officer in Relation to Money Laundering & Terrorism Financing
4. Complaints from Clients
5. Compliance Independence
6. The Compliance Officer’s Relationship with the Firm and Regulators
7. Compliance reporting
Section 2/60%
Topic 4: Establishing and Monitoring Compliance
1. Developing a Comprehensive Compliance Programme
2. Effective Compliance Infrastructure
3. Dealing with Conflicts of Interests
4. Reporting Line and Audit Trail
5. Review of Compliance Programme
Topic 5: Risk Management
1. Introduction to Risk Management
2. Risk Management in a Fiduciary Relationship
3. Risk Management Infrastructure
4. Tools for Risk Management
5. Ethics of Risk Management
Topic 6: Costs and Benefits of Compliance and Case Studies
1. The Costs of Compliance
2. The Benefits of Compliance
3. 1987 Equity Market Crash
4. 1991 Junk Bond Debacle
5. 1997 Long-Term Capital Management Debacle
6. Sumitomo
7. 1997-98 Asian Financial Crisis and Economic Crisis
8. The Financial Crisis of 2007-2009
Section 3/20%
Topic 7: Structural Framework and Principles of Capital Market Regulation
1. Framework
2. Principles of Regulations
3. Single Licensing Framework for the Capital Markets
Topic 8: Guidelines for Compliance
Answer: C
Sample Questions
Sample Question 1
Which of the following are elements of good corporate governance?
I. Promotion of shareholders’ rights
II. Investor education
III. Promotion of shareholders’ responsibilities
IV. Controlled access to the management of the company
A. I and III only
B. II and IV only
C. I, II and III only
D. All of the above
Answer: C
Sample Question 2
Which of the following is TRUE about segregation of assets in stockbroking firms?
I. All client’s asset should be segregated from Participating Organisation’s assets except
for collateral assets
II. All client’s asset should be completely segregated from company’s assets
III. Client’s fund should be completely segregated from Participating Organisation’s fund
unless there is written instruction from clients to combine the fund
IV. Participating Organisation’s account should be completely segregated from client’s
account
A. I and III only
B. II and IV only
C. I, II and IV only
D. All of the above
Answer: B
Sample Question 3
Which of the following BEST describes the scope of compliance?
(A) Compliance in the context of the capital market refers to compliance to the internal
policies and procedures of a firm
(B) Compliance by a firm is limited to ensuring compliance to the rules and regulations
stipulated by the regulators
(C) Compliance goes beyond ensuring compliance to the rules and regulations but also
encompass compliance to the firm’s own standards, process and procedures
(D) Compliance refers to compliance to decisions by the board of directors or shareholders
of the firm
Answer: C
Sample Question 4
The following are best approaches in monitoring a firm’s adherence to and effectiveness of
an internal compliance programme EXCEPT:
(A) monitoring should take the form of periodic, audit-style compliance procedural reviews
(B) monitoring should require daily reports to detect potential non-compliant trading
activity
(C) monitoring function should be solely the responsibility of the Compliance Officers and
the Board of Directors
(D) monitoring should continuously be done in tandem with the developments in rules and
regulations governing the market
Answer: C
Sample Question 5
Select statements which are CORRECT pertaining to Compliance Culture.
I. Ultimate responsibility for embedding a compliance culture within a firm lies with the
Compliance Officer
II. Compliance Culture of a firm differs from one firm to another
III. Compliance Culture of a firm arises from the firm’s values, attitudes and beliefs
IV. Comparing the process procedures and administration of the firm with principles of
compliance may determine whether a firm is pro-compliance or anti-compliance
A. I and II only
B I, III and IV only
C II, III and IV only
(D) All of the above
Answer: C
Note:
The purpose of this module is to provide candidates with an overview of the requirements for compliance in the Malaysian capital market. Candidates will gain a working knowledge of the regulatory framework and principles. It will allow students to identify the risks and issues to be addressed in establishing a comprehensive compliance programme.
Learning outcomes
Upon completion of this module, you should be able to:
Candidates are expected to have good knowledge, understanding and ability to apply in the
following areas:
• The fundamentals of compliance
• The principles of compliance
• The role, function, responsibilities and duties of Compliance Officers
• Compliance programme
• The interaction of roles and responsibilities which create a compliance culture
• The costs and benefits of compliance
• The concept of risk management
• Risk to workplace activities in terms of assessment and management
• The structural framework of capital market regulation and compliance
• The various guidelines for compliance and best business practice
Fundamentals of Compliance
1. Which of the following statements CORRECTLY describes the aims of a compliance programme?
I. To prevent breaches of laws and regulations
II. To promote a compliance culture within the firm
III. To maintain integrity of the firm’s dealings and business practices
IV. To enable identification and rectification of breaches of laws and regulations
A. I and III only
B. II and IV only
C. I, II and IV only
D. All of the above
Answer: D
Additional questions
1. The International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO) had set out 38 Principles of securities regulation in the IOSCO Objectives and Principles of Securities Regulation (June 2010). The 38 Principles are based on the objectives of securities regulation which are to:
I. protect investors
II. ensure markets are fair, efficient and transparent
III. reduce systemic risk
A, I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II an III only
D. I, II and III
Answer: D
2. The principles inter-relate and are all necessary within the firm for a compliance culture to evolve effectively. The principles of compliance are:
I. to comply with all laws and regulations;
II. to set up, administer and monitor the internal processes applicable to the conduct of the business activities
III. to instil a compliance culture within the firm
IV. to instil investor confidence and promote the development of the Malaysian capital market.
A, I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II, III and IV only
D. All of the above
Answer: D
3. The essential elements of an effective compliance programme are:
I. to design and establish a comprehensive programme;
II. to educate and train all staff and work with senior management to instil a compliance culture;
III. to constantly review the programme including regular reporting;
IV. to provide advice; and to work with the senior management so that there is open communication within the firm.
A, I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II, III and IV only
D. All of the above
Answer: D
4. A compliance programme aims to:
I. prevent breaches of laws, regulations, codes, internal policies etc.
II. maintain the integrity of the firm’s dealings and business practices
III. enable identification and rectification of such breaches
IV. promote a culture of compliance within the firm.
A, I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II, III and IV only
D. All of the above
Answer: D
5. Every person in a firm should be concerned with compliance, especially persons who hold the following positions including senior management staffs. Which is the following person is less important for the compliance concerned in a firm.
A. Board member
B. Chief Executive Officer
C. Support staff for business development
D. Holder of a capital market’s representative licence
Answer: C
6. Identify a true statement about a compliance-based culture.
A. A compliance-base culture is perceived to have a more flexible and far-sighted corporate environment.
B. A compliance-based culture recognizes that where a rule does not apply, a firm must rely on the personal integrity of its workforces when decisions need to be made.
C. A compliance-based culture is one that reinforces a particular set of values rather a particular set of rules.
D. A compliance-based culture is only as strong and as precise as the rules which workers are expected to follow.
Answer: D
Roles And Responsibilities
1. Select from the following the person(s) who are ULTIMATELY responsible for ensuring compliance in a firm:
A. Management
B. Audit Committee
C. Board of Directors
D. Compliance Officer
Answer: C
2. Which of the following statements are TRUE of the relationship between a Compliance Officer and the Internal Audit department?
I. The Internal Audit department reports directly to the Head of Compliance
II. They complement each other and work towards achieving a high standard of compliance
III. Both functions are responsible to assess the suitability and
independence of external auditors
IV. Compliance Officers may use internal audit reports to identify compliance issues within the firm
A. I and II only
B. II and IV only
C. I, II and IV only
D. All of the above
Answer: B
Compliance Officers
1. The following are TRUE of the responsibilities of a Compliance Officer, EXCEPT:
A. Maintaining a record of all compliance advice given to the firm
B. Assisting in the formulation and delivery of compliance training in the firm
C. Evaluating risk and monitoring the effectiveness of the firm’s internal controls
D. Monitoring the firm’s activities to ensure activities are in compliance with applicable rules and regulations
Answer: C
2. Which of the following statements ACCURATELY describes the importance of compliance monitoring to a firm?
I. It provides oversight on the firm’s financial reporting process
II. It provides continuous assessment of the efficacy of the firm’s compliance programme
III. It ensures that the firm’s compliance programme evolves with changes in the regulatory environment
IV. It ensures that the firm’s financial and accounting system represents a true and fair view of its financial position
A. I and IV only
B. II and III only
C. II, III and IV only
D. All of the above
Answer: B
3. Compliance officers requirements on ESG:
I. Upskilling and deep learning to gain a better understanding of sustainability
II. Collaborating with subject-matter experts to better navigate the ESG sphere
III. Reviewing sustainability policies and procedures to integrate organisation-wide compliance
IV. Challenging existing ESG targets to ascertain whether these targets address the chief environmental impact caused by their respective organisations
n
A. I and IV only
B. II and III only
C. II, III and IV only
D. All of the above
Answer: D
Establishing and Monitoring
1. While the existence of written procedures is mandatory, what else is required for a comprehensive compliance programme?
I. Review
II. Monitoring
III. Appropriate management structure
IV. Approval by internal audit department
A. I and III only
B. I, II and III only
C. II, III and IV only
D. All of the above
Answer: B
2. With reference to the Capital Market Services Act 2007, a firm can make withdrawals from Clients’ trust account for which of the following purpose?
I. Making payment for defraying brokerage
II. Invest on deposit at interest with a licensed banks
III. Invest on deposit with approved clearing house for a derivatives exchange.
IV. Making payment in accordance with the written instruction on a person entitled to the monies.
A. I and IV only
B. I and III only
C. I, II and III only
D. All of the above
Answer: D
3. The following statements are TRUE of the responsibilities of a Compliance officer in relation
to preventing bribery and corruption, EXCEPT:
A. Reviewing charitable and philanthropic donations
B. Training the staff on the firm’s anti-bribery and corruption policy
C. Assisting to formulate a policy on bribery and corruption prevention
D. Reporting to the firm’s Audit Committee of any bribery or corrupt practice detected
Answer: D
4. Which of the following should be included in a firm’s Code of Ethics/Conduct?
I. An ethical decision framework to assist staff in making decisions.
II. Generic examples of what constitutes acceptable and unacceptable behaviour.
III. Explanation on the firm’s expectations on the behaviour standards expected of staff.
IV. Enforcement and implementation mechanism addressing accountability and discipline for unethical behaviour.
A. III only
B. III and III only
C. I, II and IV only
D. All of the above
Answer: D
5. The staff affirmation process requires employees of the firm to declare and disclose
which of the following information to the Compliance Officer?
I Any outside directorship held by the employee
II Employees’ client list from his previous employment
III Any bankruptcy proceedings taken against the employee
IV Understanding of their job functions and responsibilities within the firm
A. I and III only
B. II and IV only
C. I, III and IV only
D. All of the above
Answer: C
6. Conflict of interest may arise in the following situations, EXCEPT:
A. Firm XYZ producing a report on Selasih Berhad to its clients while holding a proprietary
position on Selasih Berhad’s shares
B. Miss Belinda, having obtained information which is not made public on DEF Berhad, trades on DEF Berhad Securities on behalf of her clients
C. Firm ABC, having obtained confidential information about its client’s business, subsequently acts for another client who is a competitor to the
first client
D. Mr. Ang, an existing board member of Teratak Berhad being appointed as a board member of Delima Sdn Bhd who is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Teratak Berhad
Answer: D
7. If physical segregation within a firm is not possible, select from the following the other forms of segregation which can be implemented by the firm.
I. Supervise
daily trading to look for suspicious or unusual trading
II. Restrict access to data processing of trades and records such as password
protection
III. Restrict access to trading room where only authorised personnel will be
allowed entry
IV. Review that appropriate records are maintained in accordance with
compliance procedures
(A) (i) only
(B) (i) and (iii) only
(C) (ii) and (iv) only
(D) All of the above
Answer: D
Additional questions
1. There are a variety of methods which can be used to manage actual or potential
conflicts of interest. Which of the following statements is not included:
I. In many cases it is sufficient if the existence of a conflict is disclosed to and/or acknowledged by the client (for example, by including disclaimers on research or other advisor documents noting the potential conflict). In other cases, there may be legal requirement on the need to obtain clients’ consent.
II. The conflict can be so acute that it is necessary to act only for one client and decline to act for another client or in the firm’s proprietary activity. For example, in a case of a hostile take-over.
III. Have procedures and rules prohibiting activity which gives rise to conflict such as front-running or rule on priority of client orders.
IV. Restrict the flow of confidential information across the firm through segregation or by having an Information Barrier Policy and by observing the Need-to-Know principle.
A. I and II only
B. II and III only
C. II, III and IV only
D. None of the above
Answer: D
2. Staff is on the private side of an information barrier if they have a continuous and legitimate business to access sensitive or confidential information held behind an information barrier, e.g. those in the Corporate Finance Department. Therefore, the Compliance Officer is required to
maintain an up-to-date record of the following EXCEPT:
I. Information barriers established within the firm
II. The information barrier status of all staff in the firm
III. The firm’s Restricted List and Watch List
A. I and II only
B. II and III only
C. I and III only
D. All of the above
Answer: D
3. Firms establish internal policies to govern personal account dealing for the following purpose:
I. to avoid conflict of interest with the firm’s clients
II. to avoid misuse of sensitive information including unpublished price sensitive information
III. to satisfy regulatory obligations and to avoid the appearance of impropriety
IV. to protect the firm’s reputation.
A. I and II only
B. II and III only
C. II, III and IV only
D. All of the above
Answer: D
4. A firm’s Personal Account Dealing Policy should normally set out the following:
I. Type of securities or derivatives accounts covered under the policy
II. Disclosure by staff of the existence of their personal investment accounts
to the Compliance department upon joining the firm and periodic updates on the same
III. Requirement for staff to obtain the necessary approval before conducting a personal account dealing transaction. In this respect, the role of the Compliance Officer is to vet the application against
the firm’s Restricted and Watch Lists
IV. The minimum holding periods for which staff are not allowed to dispose of securities under certain circumstances. This is especially relevant where the staff is on the private side of an information barrier.
A. I and II only
B. II and III only
C. II, III and IV only
D. All of the above
Answer: D
5. A firm’s Personal Account Dealing Policy should normally set out the following. Which of the
following statements are TRUE about the content of a Personal Account Dealing Policy?
I. Type of securities or derivatives accounts covered under the policy
II. Disclosure by staff of the existence of their personal investment accounts to the Compliance department upon joining the firm and periodic updates on the same
III. Reporting of the Personal Account Dealing post-execution by the staff; and
IV. Disciplinary consequences for failing to adhere to the policy.
A. I and II only
B. II and III only
C. II, III and IV only
D. All of the above
Answer: D
6. Which of the following statements may give rise to situations of conflict of interest between the staff and the firm and possibly even a conflict with the clients of the firm.
I. Appointment to the Board of Directors of a company which is involved in a similar business as the firm;
II. Appointment to the Boa
rd of Directors of a company which supplies the firm with services or goods;
III. Working as a part-time salesman of a direct marketing company; and
IV. Holding an official position in a political party or a partisan non-governmental organisation.
A. I, II and III only
B. II, III and IV only
C. All of the above
D. None of the above
Answer: C
7. A firm’s Outside Business Activities Policy should normally set out the following EXCEPT:
I. Scope of the policy. Certain activities such as sporting clubs, resident and school associations are normally automatically exempted from the policy.
II. Requirement for staff to disclose their outside business activities to the Compliance department upon joining the firm and for periodic updates to be given.
III. Requirement for staff to obtain necessary approval before taking part in any outside business activities; and
IV. Disciplinary consequences for failure to adhere to the policy.
A. I, II and III only
B. II, III and IV only
C. All of the above
D. None of the above
Answer: D
Risk management
1. If the Memorandum of Articles of Association of a firm allows it to borrow and raise money in such manner as the firm thinks fit, which of the following is the MOST important type of risk that the firm should consider?
A. Ethical risk
B. Legal risk
C. Market risk
D. Credit risk
Answer: D
2. Which of the following should be included in a firm’s compliance programme to manage risk?
I. Policy and process on managing conflict of interests
II. Contents of training programmes on risk management
III. Clear definition of relationships between staff within the firm
IV. Policy and process on “know your product” and “know your client”
A. I and IV only
B. II and III only
C. I, III and IV only
D. All of the above
Answer: C
Costs benefits of Compliance and Case Studies
1. A compliance programme reduces the risk of potential and severe consequences of failure to comply with the law, rules of the exchange or appropriate business conduct.
There are many benefits of compliance, including:
I. Better management of risk (due to effective compliance and prudential requirements), particularly operational risk, can enhance risk-adjusted returns and provide greater certainty in managing cash flow.
II. Reduction in the incidence of disciplinary actions imposed on a firm such as fines or suspension from trading which may disrupt business as well as damage the firm’s reputation.
III. Removal of the fear of litigation and the fear of imposition of penalties (some of which are personal) for failure to comply.
IV. A reduction in customer complaints and the costs of restitution and the time taken to “put things right”.
A. I and II only
B. II and III only
C. I, III and IV only
D. All of the above
Answer: D
2. A compliance programme reduces the risk of potential and severe consequences of failure to comply with the law, rules of the exchange or appropriate business conduct.
There are many benefits of compliance such as a basis for updating employee knowledge on legal and other changes in a regular and formal manner. Which of the following statements are not related to the benefit of compliance?
I, Protection of business assets by decreasing the occurrence of unintentional errors or unethical or unfair practices (such as fraud) through quick detection and rectification and thus, a reduction in operating costs and financial risk.
II. An enhancement of the company's reputation (particularly in comparison with the consequences of failure) and the reputation of its staff. This has a flow-on effect in terms of employee morale and the ease of attracting competent employees.
III. Public confidence in the integrity of a firm can foster relationships with business partners.
IV. The adoption of high standards assists the minimisation of credit, systemic and operational risk, which promotes long-term development in the industry.
A. I, II and III only
B. II, III and IV only
C. All of the above
D. None of the above
Answer: D
Structural Framework and Principles of Capital Market Regulation
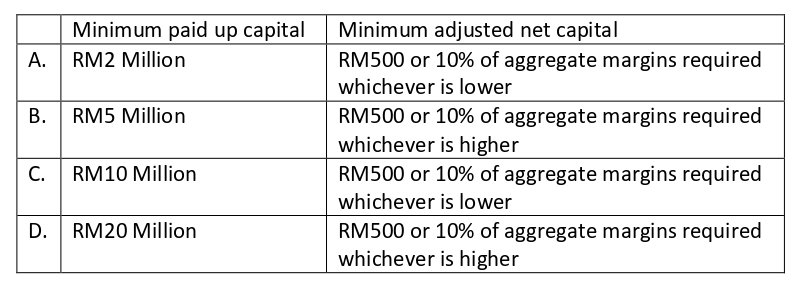
1. Select from the following the minimum paid-up capital requirement for a
stockbroking company.
A. RM2 million
B. RM5 million
C. RM10 million
D. RM20 million
Answer: D
2. Select from the following the minimum financial requirements to be maintained by Trading Participants.