This examination is designed to test candidates’ knowledge and understanding of the rules and
regulations governing advisory services in the Malaysian capital market. It is one of the
examinations to be passed by individuals who:
(1) intend to apply for a Capital Markets Services Representative's Licence (CMSRL) to carry
on the regulated activities of advising on corporate finance or investment advice;
or
(2) intend to be employees of registered persons who carry out the capital markets activities
as stipulated in Item 2 and 3 of Schedule 4 of the Capital Markets and Services Act 2007.
Candidates are advised to refer to the Licensing Handbook for the detailed combination of
examinations required for each regulated activity.
Candidates are expected to possess good knowledge and understanding of the subject matter
provided in the study outline and specified references.
In addition, candidates are expected to
have relatively strong capability in the application, analysis and evaluation of information in this
study outline and its references. It is estimated that this module will require a minimum of 200
hours of study time. Candidates may need less or more depending on the education background
and work experience.
Candidates are expected to update themselves with the latest changes relevant to this
examination as all questions will be continuously updated to reflect these changes. Candidates
are permitted to refer to their own prescribed reference materials during the examination. Note
that no prescribed reference materials will be provided by the Securities Industry Development
Corporation (SIDC). The prescribed reference materials brought into the examinations by
candidates are subject to the terms and conditions of SIDC, details of which are set out in the
terms and conditions of the SC licensing examinations.
Candidates are required to comply with the terms and conditions of the SC licensing examination.
Severe penalties will be taken against candidates for any misconduct during the examination.
At the end of this study outline are 4 sample questions of various formats used in the Module 19
examination. The samples provided do not in any way reflect the level of difficulty or the subjectmatter distribution of the actual examination. They are merely intended to familiarise candidates
with the styles of multiple-choice questions used in the examination.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Candidates are expected to have good knowledge, understanding and ability to apply in the
following areas:
(a) The principles of contract law and relevant issues.
(b) The laws which are relevant to the advisory services in the Malaysian capital market.
(c). The system and procedures of licensing of persons who carry on the investment advisory
business in Malaysia.
(d) The features and prohibitions of investment advisory activities
(e) The regulations governing the issue and offer of equity securities, listing of corporations and
quotations of securities on the Main Market of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad (Bursa
Securities) (Main Market) and proposals which result in a significant change in the business
direction or policy of corporations listed on the Main Market under the Securities Commission
Malaysia’s Equity Guidelines.
(f) The regulations setting out who can act as principal advisers for the submission of corporate
proposals and the competency standards required.
(g) The regulations governing the conduct of due diligence for corporate proposals by issuers,
advisers and experts.
(h) The activities and current trends connected to money laundering and terrorism financing and
the Malaysian regulatory approach towards them
(i) The characteristics and regulations governing take-overs in Malaysia.
(j) The regulations governing valuations of property assets in conjunction with corporate
proposals for submission to the Securities Commission Malaysia or for inclusion in prospectuses
and circulars.
(j) The regulations governing the issuance and registration of prospectuses.
(k) The regulations governing the issue, subscription, purchase, invitation to subscribe or
purchase corporate bonds or sukuk to retail investors.
(l) The regulations that must be observed for the purposes of exclusively making available
unlisted capital market products to sophisticated investors in Malaysia or persons outside
Malaysia.
(m) The regulations governing the issuers of structured warrants.
(n) The regulations governing listing of securities under the Bursa Securities Main Market Listing
Requirements, Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad ACE Market Listing Requirements and Bursa
Malaysia Securities Berhad LEAP Market Listing Requirement.
EXAMINATION SYLLABUS
The syllabus for this examination is divided into 3 sections and the maximum composition of questions from each section is as follows:
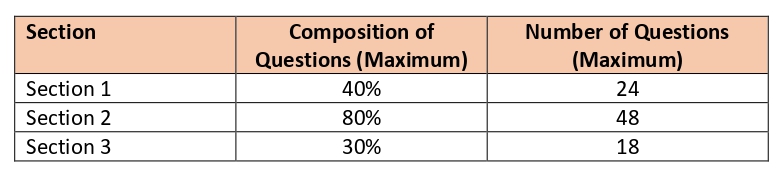
Type of questions: Multiple-choice
No. of Questions: 60
Duration: 120 minutes
Pass Mark: 70%
The Securities Industry Development Corporation (SIDC) offers multiple choice question examinations for individuals wishing to undertake one or more regulated activities under the Capital Markets and Services Act 2007.
References:
SAMPLE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Example 1
Under the law of contract, _________________ is the exchange for the promise given.
(A) intention to create legal relations
(B) genuine consent
(C) agreement
(D) consideration
Example 2
Issuance of Sukuk Islamic Securities involving a partnership arrangement between two or more
parties to finance a business venture whereby all parties contribute capital either in the form of
cash or in kind for the purpose of financing the business venture. Any profit derived from the
venture will be distributed based on a pre-agreed profit sharing ratio, but a loss will be shared on
the basis of capital contribution.
The above describes the Islamic principle of:
(A) Musharakah
(B) Mudharabah
(C) Murabahah
(D) Istisna’
Mudharabah (profit-loss sharing business) is a type of business agreement between two parties where one party provides capital (Rabb-ul-Maal) and the other labor or management (Mudarib) for the business. It helps finance businesses based on profit sharing without involving any riba or interest. Hence, it forms a Sharia-compliant mode of financing.
Murabaha, is referred to as cost-plus financing, is an Islamic financing structure in which the seller and buyer agree to the cost and markup of an asset. The markup takes place of interest, which is illegal in Islamic law. As such, murabaha is not an interest-bearing loan (qardh ribawi) but is an acceptable form of credit sale under Islamic law. As with a rent-to-own arrangement, the purchaser does not become the true owner until the loan is fully paid.
Murabaha, is referred to as cost-plus financing, is an Islamic financing structure in which the seller and buyer agree to the cost and markup of an asset. The markup takes place of interest, which is illegal in Islamic law. As such, murabaha is not an interest-bearing loan (qardh ribawi) but is an acceptable form of credit sale under Islamic law. As with a rent-to-own arrangement, the purchaser does not become the true owner until the loan is fully paid.
Example 4
In relation to the right of appointment of principal advisers, what are the rights reserved for the
Securities Commission Malaysia?
(i) Right to request for the appointment of an independent adviser
(ii) Right not to allow submissions by the principal adviser in cases where the Securities
Commission Malaysia considers the principal adviser to be incapable of giving impartial
advice
(iii) Right to decline submissions of the principal adviser where the principal adviser has an
interest in the outcome of the proposal
(iv) Right to appoint a new principal adviser in place of the existing principal adviser
(A) (i) and (iv) only
(B) (i), (ii) and (iii) only
(C) (ii), (iii) and (iv) only
(D) All of the above
Self-Assessment Questions:
CONTRACTUAL ISSUES
Question 1
Which of the following items are the essential elements of a contract, YES or NO?
Elements:
Intention (YES)
Written terms (NO)
Acceptance (YES)
Consideration (YES)
Invitation to treat (NO)
Offer (YES)
Agreement (YES)
Question 2
Brochures – Quotation – Display of goods on a shelf
The above items are all example of AN INVITATION TO TREAT.
Question 3
Identify whether the following statements on limiting and excluding liability under the common law are TRUE or FALSE.
Statements
In practice, limiting clauses are used as a defence while excluding clauses are often used to define the obligation of the parties to the contract. (TRUE)
It is sufficient for a party seeking to rely on a limiting or excluding clause if the party implies this intention. (FALSE)
The party relying on a limiting or excluding clause must adequately bring it to the attention of the other party before the contract was concluded. (TRUE)
Question 1
Describe the essential components of the tort of negligence listed below:
1. DUTY:
Answer: There must be a duty owned by the defendant to the complainant
2. BREACH OF DUTY:
Answer: There must have been a failure to attain that standard of care, prescribed by the law.
3. DAMAGE OR INJURY RESULTING FROM THAT BREACH:
Answer: Some direct and consequential loss must have been suffered by the complainant which is causally connected to breach in particular and must be recognized by the law
Question 2
Identify whether the following statements on the general liability of stockbrokers are TRUE or FALSE?
1. A stockbroker’s duty can be subjected to contractual principles. TRUE
2. From a tort perspective, a stockbroker may be liable for failing to use skill and diligence, which a reasonably competent and careful stockbroker would exercise. TRUE
3. Common law provides that if a customer suffers loss by a stockbroker’s breach of duty, it must be proven that the stockbroker had acted fraudulently. FALSE
4. In the investment market, the mere fact of losses suffered by a third party can in itself be evidence of negligence on the part of a broker. FALSE
Question 3
Any of parties as set out in Section 248 of the Capital Markets and Services Act 2007.
1. The issuer and each director of the issuer at the time issue of the disclosure document or prospectus.
2. A person who consented or caused himself to be named and was named in the disclosure document or prospectus given to an investor as a director or as having agreed to become a director either immediately or after an interval of time.
3. A promoter, for any loss or damage arising from the disclosure document or prospectus or any relevant portion of the disclosure document or prospectus in respect of which he was a party to the preparation thereof.
4. A person other the issuer, who was responsible for preparing the disclosure document or prospectus, or responsible for conducting the due diligence of the information or statement contained in the disclosure document or prospectus, by whatever name called and may include the principal adviser or lead arranger.
5. A person named in the disclosure document or prospectus with his consent, as having made statement, that was included in the disclosure document or prospectus or on which a statement made in the disclosure document or prospectus was based, for any loss or damage caused by the inclusion of the statement in the disclosure document or 387 prospectus.
6. A person named in the disclosure document or prospectus with his consent as a stockbroker, sharebroker, underwriter, auditor, banker or advocate of the issuer in relation to the issue od, offer for subscription or purchase od, or invitation to subscribe for or purchase, securities and who had made a statement that was included in the disclosure document or prospectus or on which a statement made in disclosure document or prospectus was based, for any loss or damage caused by the inclusion of the statement in the disclosure document or prospectus; or
7. A person who authorized or caused the issue of any disclosure document or prospectus in contravention of section 246, for any loss or damage caused by such contravention.
Question 4
ABC Investment Bank is the Adviser for a corporate transaction undertaken by Company X. As a result of the ABC Investment Bank’s negligence in providing advice on the transaction, Company X incurred certain hardships and financial losses amounting to RM1,500,000. Company X filed and won a lawsuit against ABC Investment Bank. The court judgement required ABC Investment Bank to pay Company X RM1,500,000 for the loss incurred. The court also required ABC Investment Bank pay RM2,000,000 to Company X, to make an example of the Bank’s wrongful behaviour. What type of damages are ABC Investment Bank paying?
I. General damages
II. Special damages
III. Nominal damages
IV. Punitive damages
A. I and III only
B. I and IV only
C. II and III only
D. II and IV only
Question 6
Robert is a client of ABC Investment Sdn Bhd, intends to claim against his dealer on the basis that he has suffered a loss having relied upon advice given by his dealer, who also did not disclose his interest in the recommended securities.
Which of the following defences can be used by the dealer?
I. The client would not have made a claim if a profit had been made.
II. The dealer was not aware of a change in the client’s investment objectives.
III. The dealer did not know that the interest existed at the e time of the recommendation.
IV. The client would have made the investment decision even if the interest had been disclosed.
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. II, III and IV only
D. All of the above
I. The client would not have made a claim if a profit had been made.
II. The dealer was not aware of a change in the client’s investment objectives.
III. The dealer did not know that the interest existed at the e time of the recommendation.
IV. The client would have made the investment decision even if the interest had been disclosed.
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. II, III and IV only
D. All of the above
