Understanding the Most Basic Concepts of Personal Finance
What is Personal Finance?
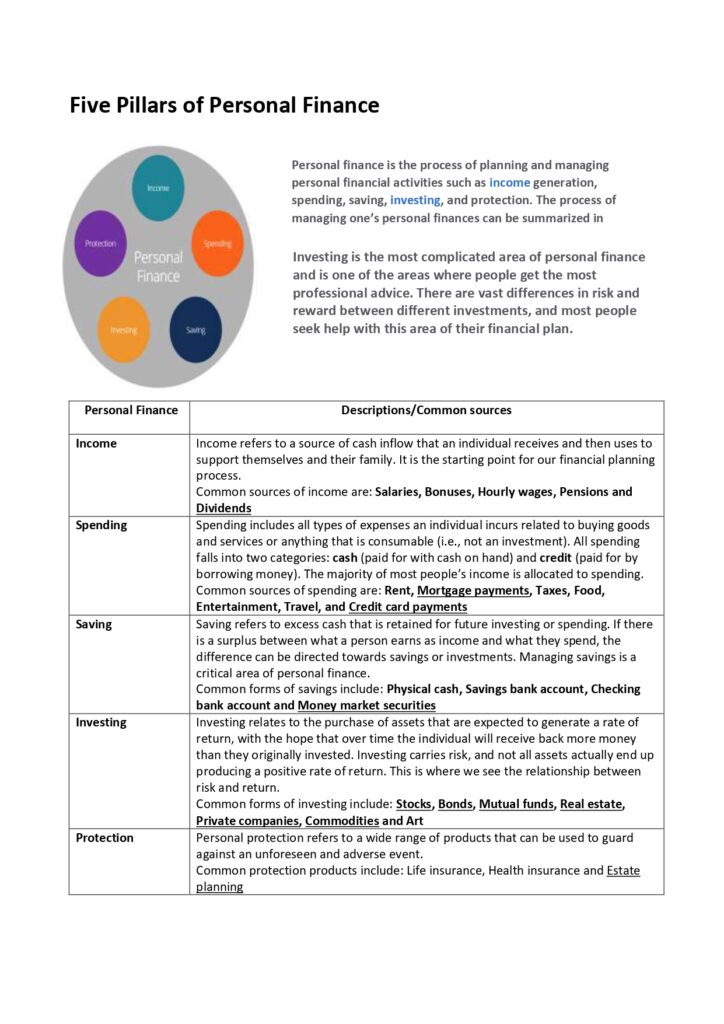
Personal finance is the process of planning and managing personal financial activities such as income generation, spending, saving, investing, and protection. The process of managing one’s personal finances can be summarized in a budget or financial plan. This guide will analyze the most common and important aspects of individual financial management...
The Importance of Personal Finance
Personal finance is about meeting your personal financial goals. These goals could be anything—having enough for short-term financial needs, planning for retirement, or saving for your child’s college education. It depends on your income, spending, saving, investing, and personal protection (insurance and estate planning)...
Components of a Good Financial Plan
A financial plan functions as a strategic roadmap, guiding individuals on how to allocate their resources efficiently to achieve specific life goals. While these goals vary for everyone, they often encompass facets like purchasing a home, ensuring a comfortable retirement, or creating generational wealth. Like a map in uncharted territory, a financial plan highlights potential challenges and offers alternate routes to reach the desired destination. Moreover, financial plans aren’t static documents. They breathe, change, and evolve with life's vicissitudes. As life's events unfold—be it marriage, the birth of a child, or a career switch—a well-structured financial plan adapts, ensuring that long-term objectives remain within reach. A solid financial plan offers immediate clarity, direction, and confidence in financial choices, reducing stress. It's more than just numbers; it's melding aspirations, values, and resources into a unified strategy, reflecting one's genuine life goals.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Financial Planning
Financial planning is one of the crucial factors to make most of your earnings. If you want to attain some financial goals, you might implement the right financial plan. So you can optimize your expenses and increase savings for post-retirement life. And without proper financial planning, you will feel several challenges to meet your financial goals. However, there are some disadvantages of financial planning as well, along with its advantages. Hence, read this article to understand the significant advantages and disadvantages of financial planning...
Consequences of Poor Financial Planning
Financial planning is a holistic exercise to evaluate your current and future financial standing and thereby enabling you to achieve all your goals in a systematic manner. A financial plan creates a road-map and equips you to meet all your life’s expenses – both the expected and unexpected. Financial planning includes budgeting your expenses, investing in right assets, setting SMART goals, selecting right asset allocation, creating a retirement plan and more...
Examples of poor financial money management
Whether you’re on a low income or earn big, not being able to manage your finances will probably bury you in debt. Financial money management might seem complicated, especially for young adults who’re just starting to learn what’s it like to earn a salary and have expenses. Making mistakes in the first few months you become financially independent is definitely ‘allowed’. Otherwise, how will you learn? But making the same bad choices over and over again can really lead to a budgeting disaster later. And there’s nothing worse than finding yourself covered in debt and unable to save for your future plans or retirement....
High Cost Of Living, Poor Financial Planning Among Reasons People Fail To Tackle Debts
The high cost of living and poor financial planning has been cited as among the main reasons Malaysians fail to pay their debts or have debt issues...
Very Few Malaysians Can Afford To Retire. What Went Wrong?
Now, about half of EPF contributors under the age of 55 have less than MYR10,000 in their accounts. And according to EPF officials, only 4 per cent of Malaysians can afford to retire. ...
WEALTH - Unit Trust & Estate Planning
What is Unit Trust?
Unit trust structures vary by region and are available in places like Guernsey, Jersey, Fiji, Ireland, New Zealand, Australia, Canada, Namibia, Kenya, Singapore, South Africa, the U.K., the Isle of Man, and Malaysia. In Asia, a unit trust is the same as a mutual fund, while in Canada, these investments are called income trusts.
Personal Monthly Budget
Expert Explains
Learn more....
Retirement Planning:
Want to Retire in Five Years?
What You Must Know
The last five years before you retire is a critical point in time—at least when it comes to retirement planning. That's because you must determine whether you can truly afford to quit working. This determination will hinge heavily on the amount of preparation you've done, and the results of that preparation....Read more
4 Things To Avoid When Planning Your Retirement
Tax Rate
(1) Revenue is used by the government to govern and manage Malaysia and its development expenditure.
(2) The Government allocates and spends tax collections for the purpose of national security, physical development and infrastructure such as roads, hospitals, schools as well as economic and social development such as health services, education and welfare of the people.
Contributed by: Alex Cheong Pui Yin
5th April 2024 (Ringgitplus.com)
































