SMEs play a vital role in shaping a country’s economy. They can be considered an attractive and huge innovative system. Due to the socially and economically beneficial effects of the SMEs, the sector is considered an area of strategic interest in an economy.
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) play a major role in most economies, particularly in developing countries. SMEs account for the majority of businesses worldwide and are important contributors to job creation and global economic development. They represent about 90% of businesses and more than 50% of employment worldwide. Formal SMEs contribute up to 40% of national income (GDP) in emerging economies. These numbers are significantly higher when informal SMEs are included.
Source: https://www.worldbank.org/
According to the World Bank’s estimates, 600 million jobs will be needed by 2030 to absorb the growing global workforce, which makes SME development a high priority for many governments around the world. In emerging markets, most formal jobs are generated by SMEs, which create 7 out of 10 jobs. However, access to finance is a key constraint to SME growth, it is the second most cited obstacle facing SMEs to grow their businesses in emerging markets and developing countries.
Source: https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/smefinance
A review of the SMEs definition was undertaken in 2013. A new SMEs definition was endorsed at the 14th NSDC Meeting in July 2013. In Malaysia, the definition covers all sectors, namely services, manufacturing, agriculture, construction and mining & quarrying.
Sales turnover and number of full-time employees are the two criteria used in determining the definition with the “OR” basis as follows:
- For the manufacturing sector, SMEs are defined as firms with sales turnover not exceeding RM50 million OR number of full-time employees not exceeding 200.
- For the services and other sectors, SMEs are defined as firms with sales turnover not exceeding RM20 million OR number of full-time employees not exceeding 75.
Detailed definition of category, namely micro, small and medium is as follows:
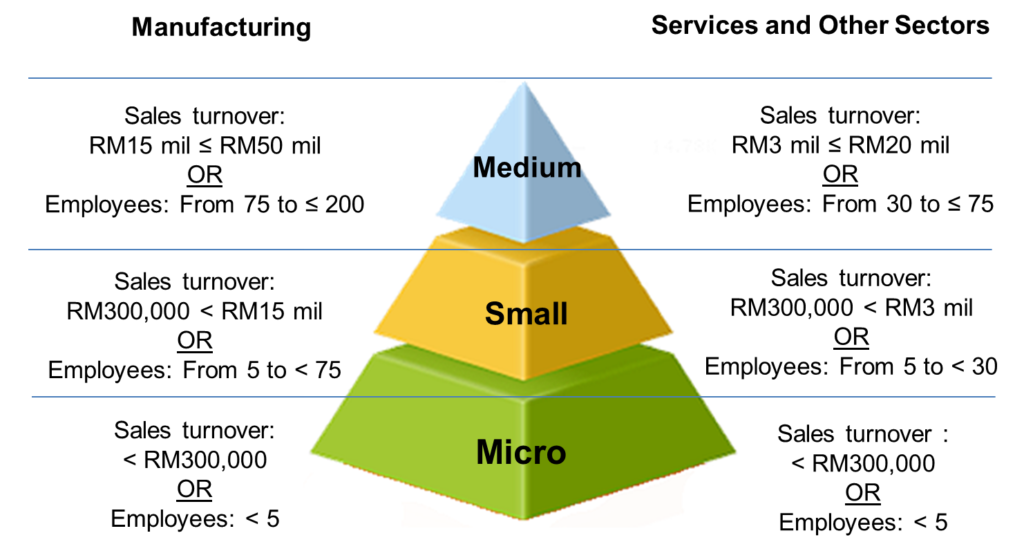
Under the new definition, all SMEs must be entities registered with SSM or other equivalent bodies. It however, excludes:
- Entities that are public-listed on the main board; and
- Subsidiaries of:
- Publicly-listed companies on the main board;
- Multinational corporations (MNCs);
- Government-linked companies (GLCs);
- Syarikat Menteri Kewangan Diperbadankan (MKDs); and
- State-owned enterprises.
SMEs in Malaysia continued to expand at a faster pace than the overall economy, despite the challenging environment faced by them in 2016. SMEs recorded a real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth of 5.2% during the year, resulting in an increase in the SME contribution to 36.6% of the country’s GDP. The SME GDP growth was reflected across all major economic sectors, mainly supported by strong tourism activity and domestic demand, led by both consumption and investment activities. In 2017, given the strong growth performance of the Malaysian economy in the first half of 2017 at 5.7%, the economy is expected to expand by more than 4.8% in 2017, higher than the earlier official growth projection of between 4.3 – 4.8%. Similarly, SME GDP growth is also expected to record a much higher growth than the earlier growth projection of between 5.5 – 6.0%. Given that the SMEs’ performance is closely linked with domestic demand and tourism activity, the anticipated pick-up in private consumption activities and increase in tourism-related activities are expected to feature more robust growth performance of SMEs in 2017.
SMEs are particularly important nowadays in any economy. They are the source of a significant share of job creation in any modern day economy. It has been seen that a large share of the unemployment reduction in many countries around the world in recent times, has been due to SMEs. These companies also contribute significantly to GDP growth around the world and also ensure that there is proper flow of money across the economy. In fact, it is these SMEs that governments rely upon to boost growth in their economies. This is true not only in Asian and African countries, but also in the US and several European countries. Given the above facts, SMEs need trustworthy logistics service providers to help them in their business. Freightarea.com is extremely helpful in this way by enabling the SMEs to be brought in touch with the relevant logistic service providers.
SMEs also charge lower rates to their clients than some of the large companies and this also allows the clients to benefit from cheaper and hence more profitable deals. Freightarea.com can enable SMEs to continue to charge lower rates as it puts them in contact with the most cost effective logistic service providers. SMEs also cater a lot to the government nowadays when it comes to defense deals and other supplies. The biggest advantage of SMEs is that it provides employment to a whole host of people, who otherwise may not have got employed.
SMEs will however thrive more when the economy does better as a whole. In case the economy is volatile, then SMEs face a risk of going under, as they all survive on a small budget. SMEs provide for boosting the level of economic growth in the country due to the extra revenue and employment that they generate. SMEs are also attractive for their clients as they provide special offers to encourage repeat business. These companies perform their activities at considerably reduced costs and so they are a very attractive way to outsource certain aspects of a company’s production process. Given that SMEs benefit from such outsourcing, it is imperative that they use the services of Freightarea.com to get hold of the best logistic services providers. This also allows other companies to have some extra capacity, which they can use to employ more workers and enhance the scale of their production. Thus, SMEs offer multiple advantages and are a great source of the growth of several countries around the world.
SMEs make up the majority of the businesses operating around the world. Generally, they are independent firms with less than 50 employees. However, the maximum number of employees is different from one country to the next. For most companies, the upper range sits around 250. Some countries dock the total number of employees at 200. The United States defines an SME, among other characteristics, as those with no more than 500 workers.
SMEs are seen as the main actors of both national and regional development in many countries. There are a lot of researches about the importance of SMEs in the country’s economy. Many countries are implemented support for SMEs in the various programs and policies. In this context, the changes were made about definition of SMEs in EU. Many programs have been implemented to improve the innovation and entrepreneurship of SMEs. Therefore, support for SMEs is one of the European Commission‘s priorities for economic growth, job creation and economic and social cohesion. SMEs play an important role in the EU economy. In addition EU is seen SMEs as an important tool in achieving the Lisbon Strategy. The importance of the SME sector is well recognized worldwide due to its significant contribution to gratifying various socio-economic objectives, such as higher growth of employment, output, promotion of exports and fostering entrepreneurship. Recent empirical studies show that SME‘s contribute to over 55% of GDP and over 65% of total employment in high-income countries. SME‘s and informal enterprises, account for over 60% of GDP and over 70% of total employment in low-income countries, while they contribute over 95% of total employment and about 70% of GDP in middle-income countries. In the European Union countries, for example, there are some 25 million small businesses, constituting 99% of all businesses; they employ almost 95 million people, providing 55% of total jobs in the private sector. Important contribution is also on exports and on productivity growth (OECD, 2004). However, the actual importance of SMEs is emerged to adapt the changing conditions of competition and innovation with the globalization process. SMEs, in many studies, are seen as key actors in innovation systems and are important in increasing the competitive and innovative capacity of the countries / regions.
Importance of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises
1. Favors flexibility and innovation
Many technological processes and innovations are attributed to small and mid-size enterprises (SMEs). Since large enterprises tend to focus on improving the old products to produce more quantities and obtain general benefits of dimensional economy, such companies are not as flexible as SMEs.
In order to be successful, SMEs focus on creating new products or services; hence, they are capable of adapting faster to the changing requirements of the market. SMEs play a vital role in shaping a country’s economy. They can be considered an attractive and huge innovative system. Due to the socially and economically beneficial effects of the SMEs, the sector is considered an area of strategic interest in an economy.
2. Creates a more competitive and healthier economy
Small and medium-sized enterprises stimulate competition for the design of products, prices, and efficiency. Without SMEs, large enterprises would hold a monopoly in almost all the activity areas.
3. Assists big enterprises
Small and medium-sized enterprises help large companies in some areas of operation that they are better able to supply. Hence, SMEs are dissolved immediately; the big enterprises will be forced to be involved in more activities, which may not be efficient for these enterprises. Activities such as supplying raw materials and distributing the finished goods created by big enterprises are developed more efficiently by SMEs.
The significance of small and medium-sized enterprises is also recognized by the governments. Hence, they offer regular incentives to SMEs, such as easier access to loans and better tax treatment.
SMEs in the United States
As mentioned earlier, the United States adheres to varying definitions for SMEs and guidelines that differ from one industry to another. The practice is in accordance with the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS). The system was collectively developed by the U.S., Canada, and Mexico to help establish a set of guidelines and standards that enable the collection and analysis of business operational statistics in North America.
The Small Business Administration (SBA) in the U.S. is responsible for creating a list of standards and characteristics that businesses must meet in order to be considered SMEs. The list is not specifically targeted for SMEs because it relates primarily to smaller companies.
However, most SMEs are required to meet all of the statutes and guidelines on the list, which also factors in the requirements and codes of operation established by the NAICS. It is important because many smaller businesses are able to apply for government contracts and funding, provided they meet all the necessary codes.
The U.S. also has a specific definition of SMEs based on the industry they operate in. For example, if a company is part of the manufacturing industry, it can be classified as an SME if it has a maximum of 500 employees, but a company involved in the wholesale trade can only have 100. Differences also exist among the sectors of an industry.
For example, in the mining industry, companies that mine for nickel or copper ore can have up to 1,500 employees, but a silver mining company can only have a maximum of 250 employees in order to be considered an SME.
Canadian SMEs
In Canada, SMEs are businesses that employ fewer than 500 individuals. Businesses with 500 or more employees are strictly considered large businesses. To further break it down, Industry Canada – an organization that works to facilitate economic and industry growth in Canada – deems small businesses as having fewer than 100 employees, provided the company produces goods. The cut-off for small businesses that provide services is 49 or fewer employees. Companies that fit somewhere between these employee-count cut-offs are considered SMEs.
Another organization, Statistics Canada – which conducts research and collects data related to businesses and commerce in the country – falls in line with the requirement that SMEs have no more than 499 employees. However, it also – based on research and data collected – stipulates that SMEs have less than $50 million in gross revenue.
Key Takeaway
Around the world, small to medium-sized enterprises make up a significant portion of the total number of global businesses. It is important to remember that while there are similarities, each country – as well as the industries and sectors within them – may adopt different definitions for an SME.
Useful links
TheWorldBank – Understanding Poverty – SMEs
Related Readings
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Small and Medium-sized Enterprises. To keep learning and developing your knowledge of financial analysis, we highly recommend the additional CFI resources below:
