What Is the Secondary Market?
The secondary market is where investors buy and sell securities. Trades take place on the secondary market between other investors and traders rather than from the companies that issue the securities. People typically associate the secondary market with the stock market. National exchanges, such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the NASDAQ, are secondary markets. The secondary market is where securities are traded after they are put up for sale on the primary market…Read more
Primary vs. Secondary Capital Markets: An Overview
The term capital market refers to any part of the financial system that raises capital from bonds, shares, and other investments. New stocks and bonds are created and sold to investors in the primary capital market, while investors trade securities on the secondary capital market…Read more
Contents
Learning Objectives
Introduction
Trading System
Rule of Bura malaysia securities Berhad on Trading
Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad Participating Organisations’ Trading Manual
Guidelines on market Conduct and Business Practices for Stockbroking
Companies and Licensed Representatives
Guidelines on Prevention of Money Loundring and Terrorism Financing for Capital Market Intermediaries
Summary
Self-Assessment
Learning Objective
At the end of this topic, you should be able to:
• Describe how securities are bought and sold using the automated trading system
• Describe a trading transaction on Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad
• List briefly the different transactions costs
• Briefly describe the requirements of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad for trading.
• Summarise the requirements and processes in the Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad Participating Organisations’ Trading Manual.
• Explain the Guidelines on Market Conduct and Business Practices for Stockbroking Companies and Licensed Representatives.
• Explain the Guidelines on Prevention of Money Laundering and Terrorism Financing for Capital Market Intermediaries.
Introduction
The secondary market is the central market place provided by Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad where investors can buy and sell existing securities.
As Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad operates with an automated trading system, we will look at trading on Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad and the automated trading system, including its basic operations and functions.
This topic finishes with a brief examination of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad, particularly those associated with trading.
TRADING SYSTEM
From 1961 to 1989, the Kuala Lumpur Stock Exchange (KLSE/the Exchange) had an open outcry system of trading. Under this system, bids and offers were shouted by the Participating Organisations’ trading room clerks to the Exchange’s board writer. The board writer then posted the bids and offers on the Exchange board. A transaction only occurred when a bidand an offer matched, and the transaction was then recorded on the board.
KLSE’s System on Computerized Order Routing and Execution (SCORE) replaced the open outcry system of trading on 13 November 1989. The Automated Trading System (ATS) compromises two major computer systems:
• SCORE, which is the central computer engine responsible for the matching of all orders
• The WinSCORE system (stockbroking company front-end trading system), which is responsible for credit control management, order and trade routing, and confirmation.
It started as a semi-automated trading system where computer terminals were situated at the Participating Organisations’ offices for order entry and at the Exchange’s trading room. Once in the system, the orders were routed to the Exchange’s matching room where they were matched by the Exchange staff. On 19 October 1992, the Exchange implemented automatic matching of orders, eliminating human intervention in the matching process.
Since 30 November 1992, the matching function has been completely automatic, and all orders are entered only at the Participating Organisations’ offices.
As of 1995, all Participating Organisations have been equipped with the exchange’s latest computerised broker front-end system known as the WinSCORE system. The WinSCORE system is used for credit control management, order and trade routing, and confirmation. The Participating Organisations can also use their terminals to view order status and monitor the Exchange’s stock market information on a real-time basis.
In 1998, the Exchange initiated new measures to ensure an orderly and fair market in the trading of Malaysian securities and to improve overall market transparency. These measures were in line with the objectives of the National Economic Recovery Plan to restore market confidence and consistent with the Exchange’s duty to ensure an orderly and fair market in securities traded through its facilities under s.98 of the Securities Industry Act 1983 (SIA), now set out under s.11 of CMSA. In upholding this duty, the Exchange is also obligated to curb and prevent activities which may amount to assisting in the establishment, operation or maintenance of a stock market that is not the stock market of the Exchange as prohibited under s.7 (1) of the SIA, now set out under s.7 of the CMSA.
In implementing these measures, Participating Organisations are required to take the necessary steps to ensure they are not assisting any persons to create another market for Malaysian securities.’
Quotation and Trading on Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad
Quotation
All securities admitted for quotation on the stock market of the Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad will be traded based on the following:
• Board(s) and classification as determined by the Exchange
• In the currency in which the securities are quoted
• In both board lots and odd lots
• On the basis of the clearing and settlement of the securities being carried in accordance with the Fixed Delivery and Settlement System (FDSS) as stipulated under Schedules 2 and 3 of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad.
• On an “ex-entitlement basis” (ex dividend, ex bonus, ex interest, ex right issue, ex all, ex offer) one clear Market Day before the Books Closing Date or such other period as determined by the Exchange
Any Participating Organisation that intends to buy or sell securities traded on Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad whether for its own account or for a client must execute the transaction:
• As an On-Market Transaction
• As a Direct Business Transaction (DBT)
• As an Islamic Securities Selling and Buying — Negotiated Transaction (ISSBNT)
On-Market Transactions and Direct Business Transactions must be executed on a Ready Basis Contract as determined by the Exchange. (Refer to Chapter 7.02 of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad)
Trading Hours and Trading Lots
The Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad Participating Organisations’ Trading Manual states that trading can be carried out from Monday to Friday (except on a day that has been gazetted as a public holiday or any other days that the Exchange is officially closed by Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad) in two trading sessions:
• Morning session — between 8.30 am and 12.30 pm
• Afternoon session — between 2.00 pm and 5.00 pm
Trading must be in a board lot or an odd lot. A board lot compromises 100 units of shares or any other number permitted by Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad to be traded. Where this number is less than a board lot, it is called an odd lot. Buying and selling quotations for odd lots must be put on the Odd Lots Board and a Participating Organisation can only sell securities in odd lots if the quantity for the sale of such securities is designated as “free securities” in the seller’s Securities Account maintained with the Participating Organisation prior to the entry of the order into the ATS (refer to Rule 7.02 (4) of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad).
Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad’s trading system limits orders to a maximum of 5,000 board lots for a single order of securities for normal lots and 99 units for odd lots (refer to Chapter 2.5 of the Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad Participating Organisations’ Trading Manual).
Types of Transactions
Trades can be cash transactions in which the financing and purchase of securities are borne by the client entirely, or margin transactions in which a client may place collateral when purchasing securities, provided that the amount of margin shall be such that the client’s equity is not less than 130% of the outstanding balance in his/her margin account (refer to Rule 7.30 (11) of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad.
Trading Orders
Before a person can trade in the shares of listed companies, he/she will first need to open the following accounts:
• A trading account (online or offline) with one of the Participating Organisations (refer to Rule 5.15 of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad on the procedures for the opening of accounts by Participating Organisations).
• A Central Depository System (CDS) account with one of the Participating Organisations (as an authorised depository agent of Bursa Malaysia Depository Sdn Bhd).
The list of persons who are eligible to open a securities account with the Depository are as follows:
o An individual who has attained the age of 18 years as of the application date
o A corporation within the meaning of s.3 of the Companies Act 2016 (CA)
o Any body corporate that is incorporated within Malaysia and is by notice published in the Gazette declared to be a public authority or an instrumentality or agency of the Government of Malaysia or of any State
o A society under any written law relating to cooperative societies
o A trustee or trust corporation duly constituted under any written law
o A society registered under the Societies Act 1966
o Statutory bodies incorporated under an Act of Parliament.
(Refer to Rule 25.02 of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Depository Sdn Bhd)
Where a nominee account is used because the client is dealing on behalf of another person, then the identity of the person must be disclosed and there can be only one beneficiary for a nominee account (s.25A (1) of the SICDA).
A nominee account is a securities account opened by an authorised nominee in accordance with the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Depository Sdn Bhd and the authorised nominee is a person who is authorised to act as a nominee as specified in accordance with the schedule prescribed under Rule 1.01, Part VIII of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Depository Sdn Bhd.
A Participating Organisation shall not deal in securities on behalf of a client if it has reason to believe that the transactions are intended to facilitate the dealing in securities or dealing in interests in securities on a stock exchange not recognised by Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad(2).
All trading must be effected through the automated and computerised securities trading system (ATS) established by Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad. Orders can only be entered by the ATS operators, who are dealer’s representatives, or trading clerks who are duly authorised by the Participating Organisation to enter orders into the ATS. The trading clerk does not represent himself/herself as a Dealer’s Representative and must strictly comply with all of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad’s guidelines, manuals and instructions relating to operational procedures of ATS(3).
All orders must be entered within a certain price range, called the upper limit price and lower limit price. These are defined in Rule 1.01 of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad. The price of orders entered into the ATS must be based on the tick size or multiples of the tick size’.
Any order entered into the ATS may be modified or cancelled by the Participating Organisation prior to the matching of the order. The modification can only be to the extent of reducing the quantity of an order. Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad may take disciplinary action available to it under Chapter 15 of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad against any participant or Participating Organisation that modifies or cancels orders with the intention to create a misleading impression of market activity.
The types of orders that may be entered into the ATS are as follows:
• Limit Order
• Market Order
• Market to Limit Order (MTL)
• Stop Limit Order
• Stop Market Order
• On-Open Order
• On-Close Order
• On Market Married Transaction (OMTT) Order
• One-Cancel-Other (OCO) Order
Please refer to Chapter 2.5.1 of the Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad Participating Organisations’
Trading Manual.
Manner of Trading
Trading Phases
There are seven different trading phases as below:
• Pre-Opening
• Opening Auction
• Main Trading Phase
• Pre-Closing
• Closing Auction
• Trading-At-Last
• End of Session/Trading Day
• Pre-Opening Phase
The pre-opening phase is an order accumulation period during which orders may be entered by Participating Organisations into the ATS. However, orders are not matched during this phase. Participating Organisations may modify or cancel any orders entered during this phase. The ATS calculates the theoretical opening price based on algorithms prescribed by Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad. Regulated Short Selling (RSS) orders are not allowed.
• Opening Auction
The opening auction is an order-matching phase during which orders in the ATS are matched.Matching of orders will be based on Price and Time Priority as below:
o Price: Buy-side orders with higher prices and sell-side order with the lower prices have higher matching priority
o Time: Where orders having the same price, then orders with earlier submission timestamps will have higher matching priority.
During the opening auction, no new orders are to be entered and existing orders cannot be modified or cancelled. The opening price is the last theoretical opening price calculated at the pre-opening phase. Where no last theoretical opening price is computed, the existing orders in the ATS will be carried forward to the main trading phase and the price of the first order matched at the main trading phase shall be designated as the opening price.
• Main Trading Phase
The main trading phase is the phase when Participating Organisations may enter new orders as well as modify or cancel orders entered. Orders entered during this phase are matched on a continuous basis. All orders which are not matched immediately upon the entry of the orders are maintained in the ATS for possible matching.
• Pre-Closing Phase
The pre-closing phase is an order accumulation period during which orders may be entered by Participating Organisations into the ATS. However, orders are not matched during this phase. Participating Organisations may modify or cancel any order entered during this phase.
The ATS shall calculate the theoretical closing price based on algorithms prescribed by Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad.
• Closing Auction
The closing auction is an order-matching phase during which orders in the ATS are matched.
During the closing auction, no new orders are to be entered and existing orders cannot be modified or cancelled. The closing price is the last theoretical closing price calculated at the pre-closing phase. Where no last theoretical closing price is or can be computed, the existing orders in the ATS will be carried forward to the trading-at-last phase and the price of the last order matched at the main trading phase shall be designated as the closing price.
• Trading-At-Last
Trading-at-last is the phase when Participating Organisations may enter new orders as well as modify or cancel orders. The price at which orders may be entered or modified is the closing price only. Orders entered during this phase are matched at the closing price.
• End of Session/Trading Day
There will be no new order entry, order modification or order cancellation permitted and no order will be matched during this session.
(Please refer to Chapter 2.4 of the Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad Participating Organisations’ Trading Manual).
Order Matching
An order will be matched based on the matching algorithm prescribed by Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad. Automatic matching of orders is done during the trading session by priority of price and then time. Market orders have priority over limit orders. A buy order at the highest price and a sell order at the lowest price have priority over other orders entered for the same securities. In the event that there are competing orders, or identical prices entered for the orders, the orders are matched in the order of time in which the orders are entered into the ATS. Each order receives a time stamp upon entry into the ATS. The time stamp shall be changed where the quantity of the order is increased or where a change is made to the price of the order (see Rule 8.08 of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad).
Direct Market Access Orders
The Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad provide that Participating Organisations may carry out Direct Market Access (DMA) transactions, which are defined as the process by which orders to buy or sell contracts including any modifications and cancellations thereof are submitted for execution in the ATS by persons referred to in Part B of Chapter 8 without any intervention by a Dealer’s Representative or being entered or re-entered by a Dealer’s Representative.
A Participating Organisation may make Direct Market Access (DMA) available to its clients and persons authorised by the client to act on behalf of the client provided it has knowledge of:
• The process of entering DMA orders
• The requirements of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad in relation to trading on the Exchange
• The relevant laws pertaining to trading on the stock market of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad5.
The Participating Organisations are considered to be the principal in relation to the DMA trades, and all DMA orders are deemed as orders submitted for execution in the ATS by a Dealer’s Representative on behalf of a client (refer to Rule 8.19 of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad).
Fees and Charges
There are several transaction costs incurred when shares are bought and sold as below.
• Commission
Commission is payable by both the buyer and the seller. The rate chargeable is dependent upon the type of instrument bought or sold (see Rule 11.02 and Schedule 6 of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad) and is based on the contract value.
Schedule 6 of Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad Commission Rates

Types of Instrument
For all trades (excluding Direct Business Transactions, instruments described in Schedule 6 and ABFMY1 trades) in stocks, ordinary shares, preference shares and other securities listed and traded on Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad executed in board lots, the brokerage payable shall be the minimum brokerage prescribed in Schedule 6 of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Berhad or such brokerage on a fully negotiated basis between the Participating Organisation and its client subject to a maximum of 0.7% of the contract value, whichever is the higher(6).
For all online routed trades or trades paid by cash upfront of securities listed and traded on Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad including Direct Business Transactions, whether on a board lot basis or otherwise, the commission payable shall be on a fully negotiated basis between the Participating Organisation and its clients and therefore the minimum and maximum commission as prescribed under Schedule 6 shall not be applicable’.
Minimum Fixed Commission
For trades other than Retail Trade, transactions denominated in Ringgit Malaysia, the Minimum Fixed Commission is (i) RM2.00 for loan instruments, and (ii) RM40.00 on any other transaction. The same amounts are the minimum commissions for transactions by employees, Dealer’s Representatives and Trading Representatives.
The Minimum Retail Commission payable by both the buyer and seller for retail trades:
• Where the contract value is RM100,000 or below, the minimum commission payable shall be calculated at 0.6% of the contract value or the Minimum Fixed Commission, whichever is the higher
• Where the contract value exceeds RM100,000, the minimum commission payable shall be calculated at 0.3% of the contract value or the Minimum Fixed Brokerage, whichever is the higher
• For an Intraday Trade, the minimum commission payable shall be calculated at 0.15% of the contract value or the Minimum Fixed Commission, whichever is the higher. Intraday Trade means buying and subsequent selling (whether or not of the entire amount bought) of securities of the same counter within the same market day.
Contract Value
Rule 11.01 of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad defines that the contract value on which commission is calculated means (a) the total value of the securities of the same counter a client purchases or sells in a market day; or if the client instructs the transaction defined as (a) above to be reflected in more than one contract, then the Contract Value is the value of securities for each contract. The value of securities is determined with reference to the price at which the securities were purchased or sold.
(a) Stamp Duty
The stamp duty is RM1.00 for every RM1,000 (or fractional part) of the transaction value of securities (payable by both buyer and seller), up to a maximum of RM200.
(b) Clearing fee
Clearing fees are payable by both the buyer and the seller at a rate as shall be determined by the Clearing House from time to time (please refer to Rule 11.05 of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad). Currently the clearing fees are as follows:
– Novated contract (On market transaction)
0.03% of transaction value (payable by both buyer and seller), with a maximum of RM1,000.00 per contract. There is no minimum fee imposed.
– Direct business contract
0.03% of transaction value (payable by both buyer and seller), with a maximum of RM1,000.00 per contract and a minimum of RM10.00.
(c) Securities Commission levy
Pursuant to the Securities Commission (Levy on Securities Transactions) Order 1995, every selling Participating Organisation and buying Participating Organisation must pay to the Exchange, for the account of the Commission, a levy on a transaction as stipulated in Schedule 7 (See Rule 11.04 (2) of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad). The rate of levy payable by a buyer or seller of securities on Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad is 0.015% of the purchase price of such purchase or sale.
Trading Procedures
The following is a brief outline of how trade transactions are effected for a client who wants to buy or sell shares starting from opening an account to delivery and settlement on Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad.
• As described earlier, before a person can trade in the shares of a company listed on Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad, he/she will first need to open a trading account with a Participating Organisationg. To trade shares in the Central Depository System, an account must also be opened with one of the Participating Organisations as an authorised depository agent of Bursa Malaysia Depository Sdn Bhd.
• Participating Organisations must also verify the client’s identity and authenticity of the application before they open a trading account for their client. (Refer to Rule 5.15 (1)(b) of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad and Directive No. 5-001, Para 9.1 of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad Participating Organisation’s Directives and Guidance on the authentication of account opening application).
• A client can only buy or sell shares through a licensed dealer’s representative. The client will give an order to the dealer’s representative to buy or sell a specified number of shares of a company at a specified price and provide his/her CDS account number for the order entry. The order is entered into the ATS, Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad’s trading system, for a possible match. A Participating Organisation must clearly identify the Securities Account where the securities arising from all dealings in the trading account must be credited into or debited from’°. The order for shares is electronically matched by the system.
• Once the order has been matched, a trade confirmation is generated at the Participating Organisation’s front-end system providing details such as order number, stock number, price and quantity of the order and counter-party Participating Organisation.
• The dealer’s representative confirms with the client that the shares have been bought or sold and informs him/her of the price.
• The Participating Organisation sends out contract notes to the client giving details of the transaction, such as brokerage (including service tax of 6%), stamp duty and clearing fees payable and the cost of the purchase or proceeds of the sale.
• The delivery and settlement of shares by the seller and buyer will then take place in line with Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad’s fixed delivery and settlement system. Under Bursa Malaysia Depository Sdn Bhd, there will be no physical delivery of shares, as a book entry delivery will be affected. The fixed delivery and settlement system will be discussed further in Topic Clearing, Delivery, Settlement and Corporate Actions.
Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad on Trading
The Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad, which relate to conduct of business by Participating Organisations (Chapter 5 of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad), address the following issues:
Standard of Conduct (Chapter 5.01)
A Participating Organisation and Registered Person must adhere to just and equitable principles and act with due skill, care and diligence and with due regard for the integrity of the market and not through any act or omission, do anything which may result in or has the effect of the market not being orderly and fair.
Conflicts of interest and risk management (Chapter 5.02)
A Participating Organisation must have in place adequate arrangements to manage all conflicts of interests and all risks that may arise in the conduct of the Participating Organisation’s business.
Structures, internal controls, policies and procedures (Chapter 5.03)
Apart of the above, a Participating Organisation must also ensure to have in place structures, internal controls and written policies and procedures designed to:
• Facilitate the supervision of the Participating Organisation’s business activities and conduct of the Participating Organisation’s Registered Persons, employees and agents
• Identify, monitor and manage conflicts of interests and risks that may arise in the course of business
• Athieve compliance with these Rules, the Directives, and the Securities Laws
• Provide for investor protection.
A Participating Organisation must consider all relevant factors in determining the adequacy and effectiveness of the Policies and Procedures. Its Policies and Procedures must always be updated by taking into account the changes in regulatory requirements, and properly disseminated and effectively enforced within its organisation.
In relation to trading, the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad also cover the following areas:
• Dealer’s representatives (Chapter 3, Part I)
• Complaints against a Participating Organisation or its dealer’s representatives (Chapter 5, Rule 5.16 (5))
• Dealings in securities (Chapter 7)
• Transactions by employees, dealer’s representatives, trading representatives and directors of Participating Organisations (Chapter 7, Part G)
• Automated Trading System (Chapter 8, Part A)
• Direct Market Access (Chapter 8, Part B)
• Regulated Short Selling (Chapter 8, Part C)
• Intraday Short Selling (Chapter 8, Part D)
• Trading Suspension (Chapter 8, Part E)
• Delivery and settlement (Chapter 9)
• Fees and charges including commission, SC levy and clearing fees (Chapter 11)
• Disciplinary Actions (Chapter 15).
Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad may exercise the following disciplinary powers against Defaulting Participants:
o To reprimand
o To impose a fine on a Participant
o To suspend a Participant from trading on the Exchange
o To strike off a Participant from the Register of the Exchange
o To impose restrictions on any activities of the Participant on such terms and for such periods as the Exchange shall think fit
o Any other action the Exchange considers appropriate, subject to consultation with the SC.
Designated Securities (Chapter 7, Part C of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad)
If in the opinion of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad, there has been manipulation or excessive speculation on any listed securities, it may, after consultation with the SC, declare those securities as designated securities. As long as the declaration remains in force, Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad may impose all or any of the following conditions:
• A margin of cover on all dealings relating to such designated securities
• A restriction on all trading in the designated securities by a Participating Organisation to the extent that the outstanding contracts of that Participating Organisation in respect of the designated securities at any one time do not exceed five per cent (5%) of the paid-up capital of the issuer whose securities have been so designated or such other percentage as Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad may from time to time direct
• A prohibition on any sale of the designated securities unless, prior to the sale, the seller has the Designated Securities designated as “free securities” in the Securities Account to be used for the sale at the time of entering into the contract
• A prohibition on the use of margin financing for purchase transactions of designated securities
• Any other condition that Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad thinks fit.
Any condition imposed shall apply to all outstanding contracts entered into before or after the date of the declaration.
Corner (Chapter 7, Part D of Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad)
If, in the opinion of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad, a corner situation has been created or arisen in a security (affected security) or control of a security has been acquired by a single interest or group, such that the security cannot be obtained for delivery on existing contracts, except at prices and on terms dictated by such interest or group, it may declare, after consultation with the SC, that a corner situation has arisen in that security.
Upon such declaration, Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad shall have the power to do any one or more of the following:
• To postpone the time for deliveries of the affected securities to such time as may be fixed by Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad or until further action by Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad
• To extend further the time of deliveries of the affected securities
• To declare that if the affected securities is not delivered on any contract at or before the time which has been fixed by Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad for such delivery, such contract shall be settled not by delivery but by payment:
o In the case of a seller who contracted to sell to the buyer at a price lower than the fair settlement price, by the seller to the buyer, of the difference between the fair settlement price and the contract price
o In the case of a seller who contracted to sell at a higher price than the fair settlement price, by the buyer to the seller, of the difference between the contract price and the fair settlement price
o In the case of a buyer who contracted to buy from the seller at a price higher than the fair settlement price, by the buyer to the seller, of the difference between the contract price and the fair settlement price
o In the case of a buyer who contracted to buy from the seller at a price lower than the fair settlement price, by the seller to the buyer, of the difference between the fair settlement price and the contract price.
The fair settlement price shall be determined by Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad and shall be binding and conclusive on all parties to any outstanding contract dealings in the affected securities. Before fixing the fair settlement price, Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad shall hear evidence from such persons as in its absolute discretion it deems necessary and proper.
RULES OF BURSA MALAYSIA SECURITIES FOR TRADING
Rule 7.01 states that a Participating Organisation’s connection to the ATS for the purpose of trading in securities on the stock market of the Exchange must be through an access point approved by the Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad and it must, at all times, take all reasonable security measures to prevent unauthorised access into the ATS. A Participating Organisation must not carry out any transaction in securities on a “Forward Contract” basis.
Direct Business Transactions
A Direct Business Transaction (DBT) is a transaction entered into outside of the Automated Trading System (ATS) and is permitted subject to compliance with conditions set out in Rule 10.01 of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad. All DBT must be delivered and settled in accordance with the fixed delivery and settlement and cleared and settled through Bursa Malaysia Securities Clearing Sdn Bhd.
All DBT shall be reported to the Exchange by the Participating Organisations by entering the details of the DBT into the ATS in the manner set out below:
• The buying and selling Participating Organisations enter the exact details of the DBT into the ATS
• The reporting of a DBT to Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad will not be accepted if one Participating Organisation fails to enter the corresponding information of the transaction
• The reporting of a DBT to Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad is confirmed on the ATS as soon as the second Participating Organisation enters the corresponding information of the DBT into the ATS within the time frame prescribed by Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad.
A DBT can be transacted at any price as agreed between the parties (see Rule 10.09 for further prescribed requirements on the price of securities transacted in DBT).
A DBT reported to the Exchange can be any of the following:
• A crossing — transaction between two Participating Organisations
• A married transaction — transaction between two clients within a Participating Organisation
• Other transactions as determined by Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad.
Margin Accounts
Trading on margin accounts refers to Participating Organisations extending credit facilities to their clients. A margin account is a trading account maintained with a Participating Organisation on which investors may borrow a percentage of the funds for the purchase of securities using the securities in the account as collateral. Read Chapter 7, Part H of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad and note the following limitations on trading on margin account:
Only Participating Organisations approved by Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad can offer such a facility (Rule 7.29)
• Credit facilities can be extended by a Participating Organisation to its clients for three months only, with rollover, if necessary (Rule 7.30 (2)). To any single client, a Participating Organisation can only extend credit facilities not more than 20% of its Effective Shareholders’ Funds (Rule 7.30 (4). Please note the definition of “single client” as stated in Rule 7.30 (5)
• Rule 7.30 (7) provides that a Participating Organisation must value any collateral that a client deposits into the clients’ margin account and any securities purchased and carried in the margin account in the manner determined by the Exchange
• Rule 7.30 (8) provides that a Participating Organisation must enter into a written agreement with its client for any margin financing extended to a client
• Rule 7.30 (11) and (12) prescribes that equity in a client’s margin account must not fall below 30% of the outstanding balance in the margin account. If the equity falls below this level, the Participating Organisation must liquidate the client’s margin account, including the securities purchased and carried in such account unless the Participating Organisation has agreed to the client’s request or proposal under Rule 7.30 (13)
• A Participating Organisations must notify the Exchange of the margin financing extended to the clients on a monthly basis in accordance with the format prescribed in Appendix 3 not later than the 10th day of each month (Rule 7.30 (21))
Contra Trading
Settlement on a contra basis refers to a Participating Organisation settling with their clients for outstanding purchase positions against outstanding sale positions of the same securities.
Rule 9.10 of the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad provides that settlement by way of contra can be effected only if a Participating Organisation has issued contra guidelines to its clients. In addition, a Participating Organisation must have in place internal guidelines to ensure that a client permitted to engage in contra transactions does not incur outstanding losses, which are not within the financial ability of the client.
Settlement on a contra basis is at the discretion of the Participating Organisation concerned.
However, if the Participating Organisation allows for settlement on a contra basis then:
• Settlement may only be effected not later than 2.00 pm on the second market day following the contract date (T+2) and such sale will be deemed to be a sale to close-off the buying client’s purchase position in respect of that securities and such close-off is referred to as “contra”. (Rule 9.09 (3))
A Participating Organisation may impose charges on its client for a contra (Rule 9.10 (3))
• Any differences resulting from a “contra” between an outstanding purchase position and an outstanding sale position shall be settled between Participating Organisations and their clients not later than the fifth market day following the date of such contra (Rule 9.10 (4)).
BURSA MALAYSIA SECURITIES BERHAD PARTICIPATING ORGANISATIONS’ TRADING MANUAL
This manual provides Participating Organisations with the relevant information relating to the operations of the Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad and pertinent procedures on dealing with Bursa Malaysia Securities.
Trading Phases and Market Timing
All buy and sell orders are keyed in by the market participants via Participating Organisations’ Order Management System (OMS) into Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad’s Automated Trading System (ATS) as per the prescribed trading Phases and Market Timing.
Market Segments
Trading of Securities is conducted in the following four market segments:
• Normal Lot Market — refers to securities traded in board lot (100 unit per lot) size and Exchange Traded Bonds and Sukuk (ETBS) securities in board lot (10 unit per lot) size.
• Odd Lot Market — securities traded in a quantity of between 1 to 99 units except for ETBS securities, which are traded in a quantity of between 1 to 9 units.
• Buying-in Normal Market — Where a Participating Organisation, having sold securities in board lots, fails by the Scheduled Delivery Time to make available in the relevant securities account, the securities in board lots as tradeable balance, the Exchange shall upon being advised by the Clearing House of the failed contract, automatically buy-in against the defaulting Participating Organisation concerned without notice, on the settlement day.
• Direct Business Transaction (DBT) Market — any share transactions effected outside Bursa Malaysia, i.e. crossing (transaction between two Participating Organisations), or married (transaction between two clients within the same Participating Organisation).
Order Entry
The quantity for a single order of securities entered into the ATS shall not exceed 5,000 board lots for normal lots and 99 units for odd lots. This rule is also applicable to buying-in transactions.
In general, the behaviour of an order is determined in the following order:
• Order Type
• Order Validity
• Order Qualification
Order Types
The following are some types of orders that may be entered by Participating Organisations into the ATS and the most basic order type is Limit Order type and Market Order type.
• Limit Order – An incoming limit order can match with multiple orders on the opposite site of the order book at prices up to the limit price specified.
(refer Appendix 1 for Examples on Limit Order Matching Rules)
• Market Order – A market order can match with as many orders as possible on the opposite side of the order book, up to the quantity carried by the market order. (refer Appendix 2 for Examples on Market Order Matching Rules)
• Market to Limit Order (MTL) – An MTL is similar to market order, except that it is executed ONLY at the best price (only the top price) available on the opposite side of the order book.
• Stop Limit Order – A stop limit order carries TWO prices, a trigger price and a limit price. It remains inactive in the order book until it gets converted to a limit order when its trigger price is reached.
• Stop Market Order – A stop market order carries a trigger price but NOT a limit price; it remains inactive in the order book until it gets converted to a market order when its trigger price is reached.
• On-Open Order – Limit-On-Open (L00) and Market-On-Open (M00) orders can only be submitted during the first Pre-Opening phase of the day and remain inactive. LOO and MOO orders are triggered at Post-Opening and before Main Trading phase starts.
• On-Close Order – Limit-On-Close (LOC) and Market-On-Close (MOC) orders can be submitted during Pre-Opening and Main Trading phases only and remain inactive. LOC and MOC orders are triggered during Pre-Closing phase.
• On Market Married Transaction (OMMT) Order – An On Market Married Transaction (OMMT) is a limit order that has both buy and sell sides and a limit price. An OMMT order matches itself and does not match with other orders in the order book.
Order Validity
The most basic order validity is the Day order validity (“Day Order”) and the Fill-And-Kill order validity (“FAK Order”).
• Day Order
An unmatched or partially matched day order will remain in the order book until the “End of Trading Day”.
• Fill-And-Kill (FAK)
An FAK order is to be matched immediately, either partially or fully; otherwise it will be cancelled by the ATS.
• Fill-Or-Kill (FOK)
An FOK order is to be matched immediately AND fully; other it will be cancelled by the ATS.
• Bursa Good-Till-Date (Bursa GTD)
A Bursa GTD order remains in the order book if it is not fully matched, from the time it is entered till it reaches its specified expiry date, cancelled by the Participating Organisation or withdrawn by the Exchange. Unmatched quantities are carried forward to the following trading day.
• Bursa Good-Till-Cancel (Bursa GTC)
A Bursa GTC order remains in the order book if it is not fully matched, from the time it is entered till it reaches the maximum expiry day specified by the Exchange, cancelled by the Participating Organisation or withdrawn by the Exchange. Remaining unmatched quantities are carried forward to following trading day.
Order Priority (Matching Priority)
The matching priorities for the orders in the order book are based on Price (the price of the order) and Time (the timestamp of the order). The buy orders will be arranged from the highest to the lowest price while the sell orders are arranged from the lowest to the highest price. Orders with the same price will be arranged from the oldest timestamp to the latest timestamp.
Modified orders with price change will queue at their new price and timestamp at which the order modification is accepted by the ATS whereas orders modified with increased quantity will queue at the same price but timestamp will change to the time when the ATS accepts the order modification. However, the queue for orders with decreased quantity will remain unchanged at the original price and timestamp.
Contract Amendment
Contract amendment is allowed under Chapter 8.09 of Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad. Participating Organisations can make amendment up till 8.00 pm on the transaction date. However, the contract amendment is only valid for trades of the same day; trades from previous days are not affected (in the case of Bursa GTD and Bursa GTC orders being matched on more than one day). Participating Organisations and their Dealer’s Representatives may amend a contract subject to the following conditions:
(a) The amendment is on the Securities Account number
(b) The amendment is a result of an error
(c) The amendment will not result in a change of the original party who placed the order and for whom the order was supposed to be executed, if not for the error
(d) The amendment is made within the time determined by the Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad.
Market Opening and Closing
During the Pre-Opening and Pre-Closing phases, “Theoretical Opening Price” (TOP) and “Theoretical Opening Volume” (TOV) for each securities is calculated by ATS and disseminated accordingly during the Pre-Opening phase while in Pre-Closing phase, “Theoretical Closing Price” (TCP) and “Theoretical Closing Volume” (TCV) are calculated for each securities. The last calculated TOP and TCP will be the opening and closing price respectively in their trading phases.
Reference Price and Price Limits
Each securities in the Normal Lot market segment has a Reference Price and Static Price Limits (Upper Limit Price and Lower Limit Price). The values for the Static Price Limits of a securities are calculated based on a specified range of percentage or absolute value from its Reference Price. The values of Reference Price, Upper Limit Price and Lower Limit Price remain unchanged throughout the trading day, except for the Reference Price and Static Price Limits for Structured Warrants, which may change from trading session to trading session subsequent to first day of quotation.
Reference Price
The Reference Price for all securities traded in Bursa Malaysia is valid for the trading day, with the exception of Structured Warrants, which is valid for the trading session during a trading day (refer to Chapter 4.2 of the Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad Participating Organisations’ Trading Manual).
Static Price Limits
Bursa Malaysia enforces Static Price Limits for all securities traded on Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad. Orders must be entered within the range of Upper and Lower Limit Price as defined by Bursa Malaysia during the trading day or session (refer to Chapter 4.3 of the Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad Participating Organisations’ Trading Manual).
Dynamic Price Limits (DPL)
Dynamic Price Limits (DPL) is a security measure by the Exchange to prevent sudden fluctuations in price movement due to trade aberration on all securities except new listings. It applies only to normal market orders and during all trading phases, except pre-open, pre-close and trading at last phase. It is also not applicable during securities halt and Circuit Breaker Halt periods.
If the DPL of a security is triggered, Participating Organisations can request to the Exchange for a temporary upliftment of the DPL of that securities, where the Exchange will issue a Special Announcement to inform the market on the temporary upliftment and its resumption time.
During the upliftment time, the orders for the securities can be matched beyond the DPL mechanism band, and only Static Limit will be in effect.
Last Price Limits (LPL)
Similar to the function of the DPL, Last Price Limits (LPL) act as a security measure on the closing price of Normal Lot market, by affecting the Theoretical Closing Price and orders entered during the pre-closing phase. It applies to all listed securities, including Initial Public Offerings (IPO)! new listings. All outstanding orders from main trading phase will be carried into the pre-closing phase, but new orders entered during the pre-closing phase must be at or within the LPL range.
There is no upliftment of LPL.
Trading Status
The Trading Status of a securities shall be specified by Bursa Malaysia as below:
• Active — active orders may be entered, modified, cancelled and matched.
• Circuit Breaker Halt (Levels 1 and 2) — when this is triggered, the Trading Status of a Securities is specified as “Halt”; orders may be entered, modified and cancelled but shall not be matched.
• Circuit Breaker Suspension (Level 3) — a securities is specified as “Suspend”; orders in respect of the securities shall not be entered, modified, cancelled or matched.
• Suspension — This status will be manually invoked upon request for suspension. A securities is specified as “Suspend”; orders in respect of the securities shall not be entered, modified, cancelled or matched.
• Halt — This status will be manually invoked upon request for suspension. Orders may be entered, modified and cancelled but shall not be matched. (Refer to Chapter 5.3 of the Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad Participating Organisations’ Trading Manual on how trac halts are implemented, Appendices 7 and for Securities Status and a summary of trading halts time and period with the impact of the trading halts for normal market, odd lot market and Direct Business Transactions).
Buying-in Transactions
Buying-in is the process of buying shares by Bursa Malaysia for settlement of failed trades on behalf of defaulters, which is instituted against the relevant selling Participating Organisation the event that the selling clients’ CDS accounts do not have sufficient securities for settlement on due date. It is only applicable for failed board lot transactions. Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad will institute buying-in against the relevant Participating Organisation on the second market day (T+2) following the date of contract under the T+2 settlement cycle from 2.00 pm to 5.00 pm in the event that the selling client’s CDS accounts do not have sufficient securities for settlement on due date. All unsuccessful buying-in will be cash settled to expedite the resolution of outstanding failed contracts under the T+2 cash settlement.
Participating Organisations may also request for a manual buying-in under the circumstances when there is failure in delivery of securities from Direct Business Transactions. There is no automatic buying-in on Direct Business Transactions.
The automatic buying-in and manual buying-in timing and prices under the 1+2 settlement cycle are as follows:
Automatic buying-in: Second session in a trading day from 2.00 pm to 5.00 pm
Manual buying-in: First session — 8.30 am to 12.30 pm / Second session — 2.00 pm to 5.00 pm
The bidding price for buying-in of any securities by the Exchange shall be 10 ticks above:
• The Closing Price on the previous trading day, or
• The Last Done Price for the previous trading session of such securities whichever is the higher, or
• The last ‘cum’ price in respect of buying-in for ‘cum’ contract on or after the Ex-date up to the close of business on the lodgement date
• In the case of untraded Structured Warrants, the Upper Limit Price at the previous trading session close, if there is an order to buy at the Upper Limit Price at the close of the session.
The buying-in price will be based on a different tick structure and tick sizes to ensure that the buying-in price is attractive to potential sellers.
Short Selling
The following types of short selling are available on Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad:
• Regulated Short Selling (RSS)
• Proprietary Day Trading (PDT)
• Permitted Short Selling (PSS)
• Intraday Short Selling (IDSS)
All short sell orders must adhere to the order type and order validity stipulated in para. 2.5.4, Chapter 2 of the Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad Participating Organisations’ Trading Manual. Short selling is only applicable for normal market, excluding OMMT and it is not allowed for odd lot, buying-in and DBT markets.
Regulated Short Selling (RSS)
RSS means the selling of securities approved by Bursa Malaysia where the seller does not own such securities but has borrowed the approved securities from an Authorised Participant prior to the execution of the sale. The Participating Organisation must ensure all conditions stated in para. 7.2, Chapter 7 of the Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad Participating Organisations’ Trading Manual are met for RSS orders. Participating Organisations must open and use a designated RSS trading account for RSS orders only, with the exceptions stated in para. 7.2.2, Chapter 7 of the Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad Participating Organisations’ Trading Manual. RSS orders must comply with the tick rules stipulated by Bursa Malaysia. The tick rules applicable to RSS orders are as follows:

The following table is the RSS order execution summary.
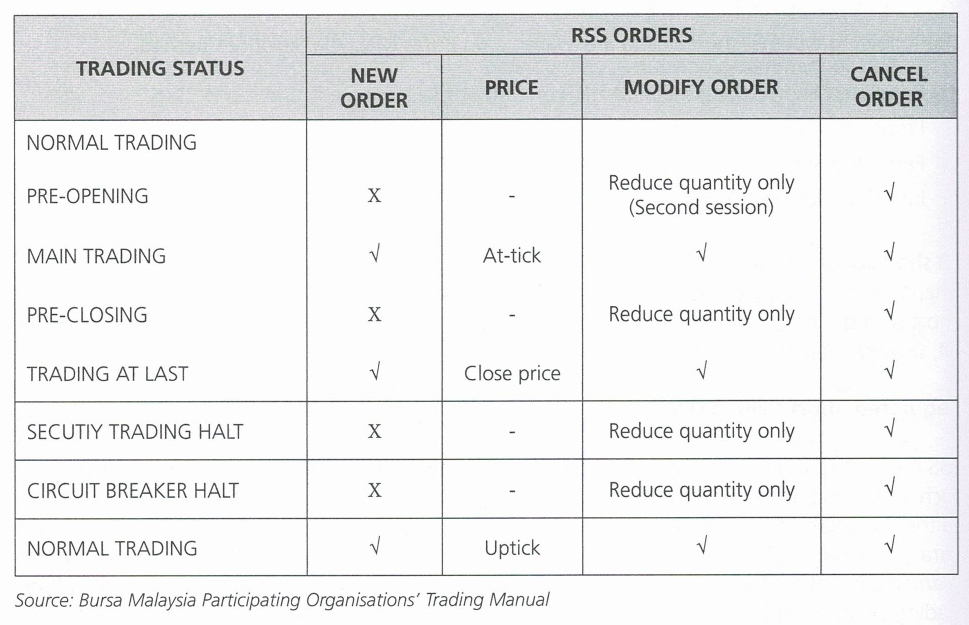
RSS Trade Limit of a particular RSS securities:
Daily Trade Limit: 3% (daily total gross volume of RSS against the issued number of shares of the said securities).
Aggregate Total Net Short Position: 10% (Total Net Short Volume of RSS against the issued number of shares of the said securities).
Once the daily RSS trade limit is reached, RSS trading for that particular securities will be suspended for the day. All existing RSS orders will also be cancelled by the trading system.
Once the aggregate total net short position for RSS is reached, RSS trading for that particular securities will be suspended until the total net short outstanding volume of the RSS trade is below the 10% limit again.
Proprietary Day Trading (PDT)
Proprietary Day Trading (PDT) dealers are allowed to enter short selling orders (PDT orders) on PDT-eligible securities. The Participating Organisation must open a designated trading account for PDT orders. A trading suspension on the RSS securities will also suspend the PDT securities, thus subsequently suspend the PDT sell orders. However, there is no tick rule requirement and Trade Limit for PDT.
Circuit Breaker
A circuit breaker is a mechanism implemented to moderate excessive volatility in the stock market of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad. It is a market-wide approach to manage downward movement of the barometer index by temporarily halting market trading during normal trading hours in order to allow the investors time to obtain more information available through all possible sources and rely less market trends and speculation, to evaluate and make well-considered investment decisions upon resumption of trading.
Bursa Malaysia Circuit Breaker Trigger Limits:
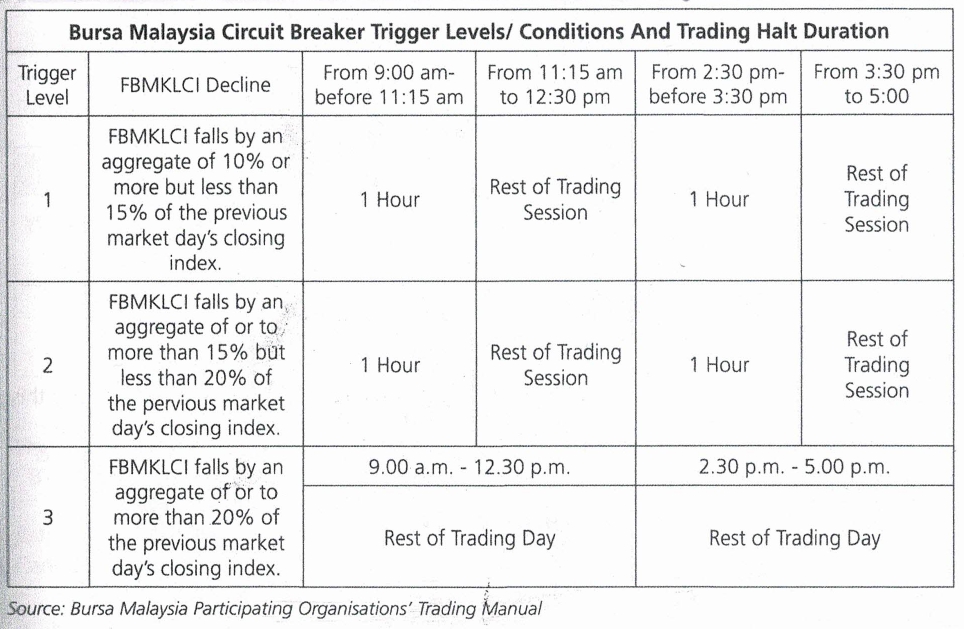
In the event that the circuit breaker hits the 3rd level, Bursa Malaysia has the discretion to either halt or suspend trading of the securities group.
The Circuit Breaker Levels will be calculated by Bursa Malaysia before the beginning of each market day using the prescribed percentages based on the closing value of the FBMKLCI of the previous market day.
During a Level 1 and Level 2 Circuit Breaker Trading Halt, the Trading phase status will be “HALT”. Limit Orders can be entered, modified or withdrawn. New Market Orders (MOs) will be rejected by the system. However, modification or withdrawal of the existing MOs can be performed. No matching will take place.
During a Level 3 Circuit Breaker Trading Halt, the status will be “SUSPEND”. Orders cannot be entered, modified, cancelled and matched.
Direct Business Transactions (DBT)
Direct Business Transactions (DBT) include transactions outside Bursa Malaysia’s ATS but reported in ATS:
• Crossing (transaction between two Participating Organisations)
• Married (transaction between two clients within a Participating Organisation)
The transaction price for DBT report is based on the following:

Participating Organisations can report DBT trades at any price subject to the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad on DBT. However,
Participating Organisations must ensure that they have a procedure/system in place to provide the PVWAP if their DBT is based on PVWAP.
DBT cannot be performed for the first hour of the trading session for securities under new listing, corporate exercise or re-quoted from suspension.
Cancellation of DBT trades is not allowed, except for “client amendment purpose” only. For this purpose, both parties involved in the DBT must cancel the trade together and replace it with a new trade accordingly. (Refer to Appendix 11 — Direct Business Transactions Amendments & Cancellation Report)
On Market Married Transaction (OMMT)
An On-Market Married Transaction (OMMT) is a trade transaction whereby a Participating Organisation can key in a buy and sell order to match directly on-market without going through the order book under the conditions stated in para. 10.1.
OMMT orders are only to be allowed during the Main Trading Phase and Trading-At-Last (TAL) phase only. During the Main Trading Phase, only limit order types are allowed, at or within the best buy and sell limit prices. An OMMT effected during the TAL phase must be at the closing price.
OMMT is provided for normal market only and the total quantity of single order OMMT must range in between the minimum and maximum quantity defined by the system. No Regulated Short Selling (RSS) and Proprietary Day Trading (PDT) is allowed.
Error Trade Policy
The Exchange’s Error Trade Policy is for the purpose of minimising the impact of error in trade to the market to ensure the functioning of a fair and orderly market. The Error Trade Policy covers the following:
(a) Price adjustment for error trades by Participating Organisations
(b) Trade cancellation arising from erroneous execution of a contract due to system failure or mistake in the entries made in the ATS, failure or malfunction in the trading system, services or facility of the Participating Organisation or unauthorised entry of an order.
Under Rule 8.12A, the Participating Organisation can only make a request for a Price Adjustment on error trades if it is matched outside the No Adjustment Range (“NAR”) and has a Potential Trading Loss of not less than RM50,000.

The Error Trade Policy is applicable to board lots only. It does not cover buying-in, odd lots and DBT.
Refer to the table below for trading phases that are eligible for Price Adjustment/Trade Cancellation requests:
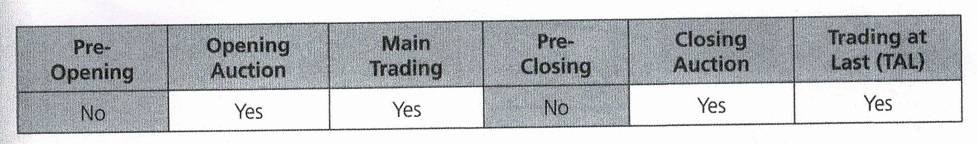
There is no matching during the Pre-Opening and Pre-Closing phases; therefore, no matched and trades for consideration.
The Exchange will impose a fee of RM1,000.00 on all approved requests for price adjustment and trade cancellation. Any trade cancelled is irrevocable.
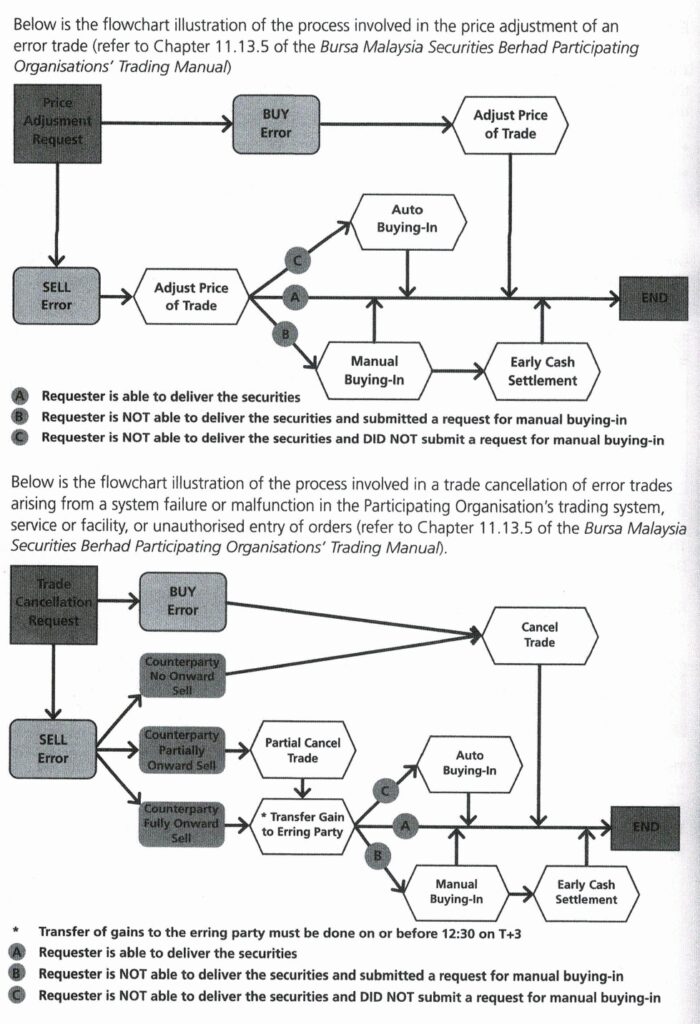
A trade cancellation of error trades can be originated from the Exchange or the Participating Organisation(s). The Exchange may immediately “Halt” or “Suspend” the entire market or a specified stock or group of stocks to ensure a fair and orderly market. Only the first level of error trades will be cancelled by the Exchange.
Order Cancellation
On an occasion whereby a Participating Organisation needs to cancel an order but its Order Management System (OMS) is down, the said Participating Organisation can submit a request to Securities & Bond Trading (SBT) of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad to cancel the said order. A Participating Organisation under an emergency will be given only an option to do a “Cancel all orders” or “Cancel orders by instrument”.
An order which is not matched will be cancelled by Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad. For orders which are partially matched, POs must accept the trade as good. The order cancellation will clear all outstanding orders in the PO’s order book.
Market Emergency
The Exchange may trigger trade suspension on specific securities groups or the entire market in the event of an emergency or disastrous situation, such as fire, computer malfunctions, system errors/programme bugs, technical glitches, power failure, or similar disruptive events, affecting
Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad and/or the Participating Organisations, that is likely to severely and adversely affect the operation of the Exchange and/or Participating Organisations and threatens the market from operating in a fair and orderly manner.
GUIDELINES ON MARKET CONDUCT AND BUSINESS PRACTICES FOR STOCKBROKING COMPANIES AND LIMITED LICENSED REPRESENTATIVES
These guidelines set out 11 principles of supervision applicable to stockbroking companies and their representatives under the SC’s principles-based regulation and the requirement to comply with the Anti-Money Laundering and Counter Financing of Terrorism (AML/CFT) Guidelines.
The SC had adopted principles based regulation in supervision and below are the 11 core principles which apply to stockbroking companies:
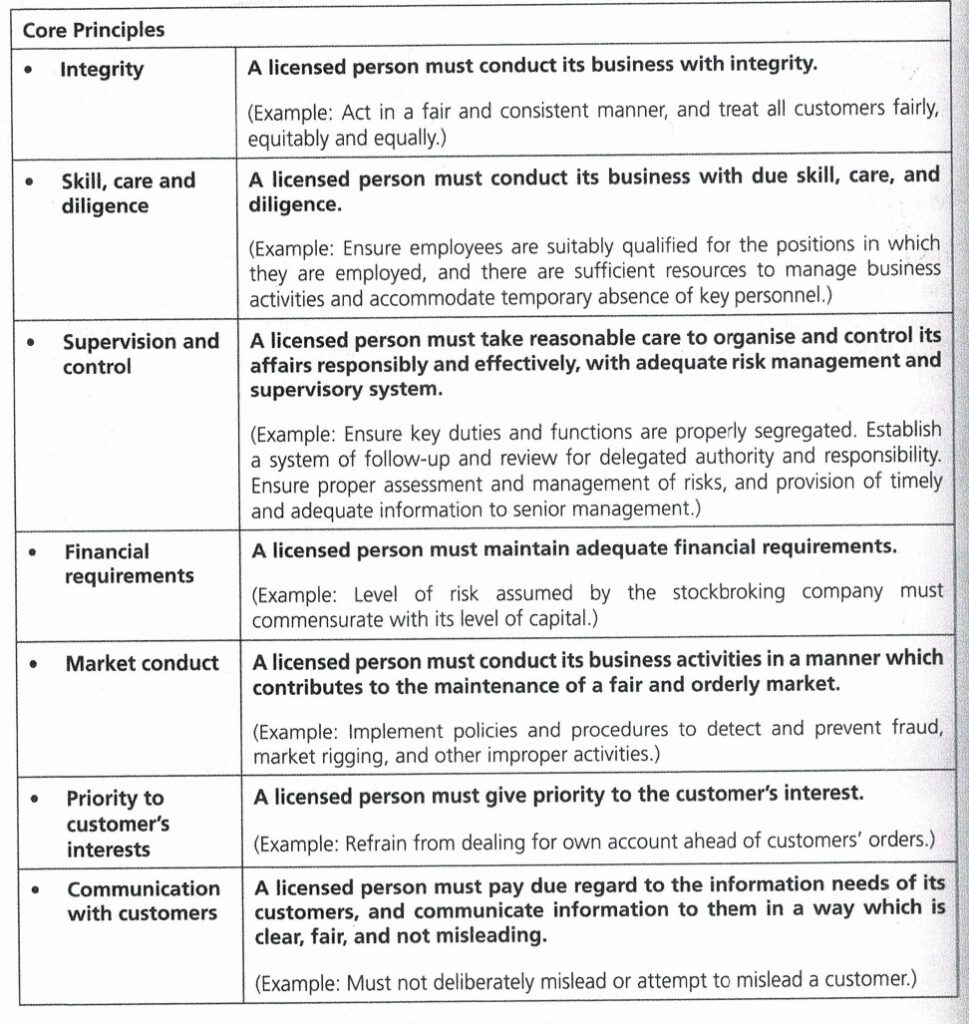
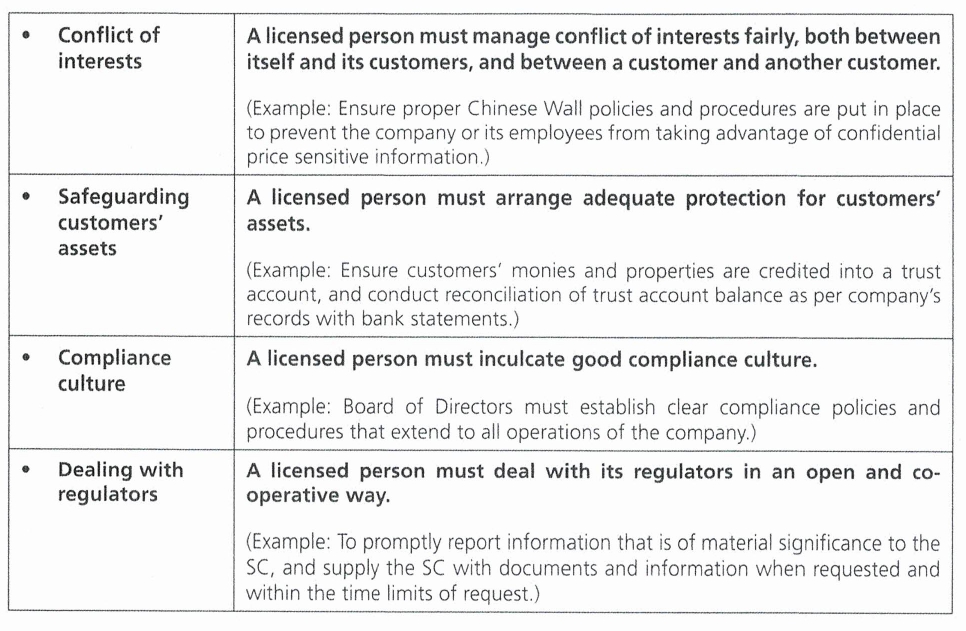
Primary Accountability and Responsibility for Compliance
The 11 core principles above set the level of regulatory standards in supervision that the SC seeks to achieve for licensed persons. Under principles-based approach, the SC will focus on the desired level of regulatory outcomes. The Board of Directors and senior management of the
stockbroking company will be held accountable and responsible to ensure adequate policies, procedures and resources are in place to meet the core principles. The level of readiness and willingness to abide by the core principles will be the main criteria in assessing a stockbroking company’s level of compliance with the core principles.
Customer Due Diligence
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) is a set of policies, procedures, processes, and controls to assist a stockbroking company to evaluate, with reasonable certainty, the identity and risk profile of customers. Proper adherence to the process would assist the stockbroking companies in detecting and reporting unusual or suspicious transactions, and minimising unscrupulous
financial transactions.
Key areas for compliance under CDD processes are:
– Adherence to AML / CFT Guidelines on CDD
– Adherence to Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad’s rules on opening of accounts — A stockbroking company and its representative should not effect any transaction on behalf of a customer unless the required CDD is conducted on the customer.
Upon the opening of customer’s account, ongoing monitoring of customer’s activity should be carried out. Enhanced COD measures must be taken on customers identified as “high risk”.
Information to Customers
The Participating Organisation and its representative should ensure the customers are in possession of all necessary information to make sound investment decision and the advice, recommendation or trading limit approval are given to customers in accordance with their financial circumstances and risk profile.
Discretionary Trades
A dealer’s representative of a stockbroking company may carry out discretionary trading on behalf of his/her customers provided that he/she has obtained prior approval from senior management of the stockbroking company and maintains a record of discretionary trades carried out on behalf of his/her customers. He/she must report details of the discretionary transactions to his/her customers on a quarterly basis. The stockbroking company should ensure adequate internal control procedures are in place to properly supervise the operation of the discretionary trades.
Unauthorised Use of Customers’ Accounts
Unauthorised use of customer accounts is prohibited. To prevent unauthorised use of customer accounts:
• Adequate policies and control must be in place to ensure changes to customer’s data are genuine
• All transactions must be issued to seller or customer directly
• Monitoring and aggregation must be done, for risk profiling purposes, on all the accounts where settlements for outstanding purchases are made or originate from one singular source
• Cheques issued to the company must always be in the <name of the stockbroking company> for <name of the customer>
A stockbroking company is prohibited from issuing cash cheques for payment of sale proceeds to the seller-customers.
Handling Error Trades
An error account should be used solely for the purpose of amending a bona fide trading error. A stockbroking company must put in place internal procedures on handling error trades, which must include the following:
• Justification to book trades into an error account
• Written approval from senior executive for using an error account
• Maintenance of proper documentation on handling error trades
• Monitoring requirements on frequency of error trades by any customer or stockbroking company’s representatives.
Managing Conflict of Interest
A stockbroking company and its representatives must disclose all potential conflict of interests to the customers and extra care must be taken to ensure information concerning any securities provided to customers has reasonable basis. The company must have sufficient supervisory and
internal controls to ensure the analysts’ research and recommendations are not compromised and non-public information are not shared with unauthorised persons.
Reporting Breaches
A stockbroking company must monitor and review the company’s operations to ensure compliance with all relevant regulations and ensure disciplinary processes are applied in a fair and consistent manner. Upon any possible occurrences of breaches of securities laws, the Head of Compliance must immediately commence internal investigations and report the outcome of
the investigations to the Board of Directors for further actions. He must notify the SC as soon as possible and extend full cooperation to regulatory authorities.
Market Abuses and Unethical Business Conduct
A stockbroking company and its representative must not carry out or facilitate any transactions that would affect the fair and orderly operation of the market. They are prohibited from getting involved in assisting customers in activities which would lead to market abuse or unethical business conduct and/or breaches of securities laws or Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad rules. Part II, Para 12.0 (b) of the Guidelines provides a list of activities which may lead to market abuse or unethical business conduct and Appendix Part III, Para 13.0 illustrates the various conducts or situations which constitute market abuses and unethical business conduct:
Action based manipulation
Trade-based manipulation
Painting the tape
Unethical trades
Rollover
Third party payment
Marking the close
Front running
Conflicts
Scalping
Spoofing
Pump and dump
Trash and cash
GUIDELINES ON PREVENTION OF MONEY LAUNDERING AND TERRORISM FINANCING FOR REPORTING INSTITUTIONS IN THE CAPITAL MARKET
Prevention of Money Laundering and …
26 Apr 2021 — 4.3. The illegal funds laundered through the capital market … or terrorism financing are identified, the reporting institution must check these…Read more
Anti-Money Laundering & Counter Terrorism Financing
1. Guidelines on Prevention of Money Laundering and Terrorism Financing for Capital Market Intermediaries. Issued: 15 January 2014. Revised: 7 December 2016…Read more
Labuan FSA – Guidelines on anti-money laundering and counter financing …
This Anti-Money Laundering and Counter Financing of Terrorism (AML/CFT) – Capital Market and Other Business Sectors Guidelines is based on the principle that…Read more
The Guidelines on Prevention of Money Laundering and Terrorism Financing for Reporting Institutions in the Capital Market are issued pursuant to s.83 and s.66E of the Anti-Money Laundering, Anti-Terrorism Financing and Proceeds of Unlawful Activities Act 2001 (AMLA) and s.158 (1) of the Securities Commission Act 1993. These Guidelines are drawn up in accordance with the AMLA and the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) 40 Recommendations, and they provide guidance for reporting institutions to comply with the obligations imposed under the AMLA.
The Guidelines covered the following information:
• Part 1 — Introduction and Applicability
• Part 1A — AMUCFT Compliance Programmes and Obligations of Board of Directors, Senior Management and Compliance Officer
• Part II — Risk-Based Approach Application
• Part III — Customer Due Diligence
• Part IIIA — Wire Transfer
• Part IV — Retention of Records
• Part V — Suspicious Transactions
• Part VI — Enforcement Orders
• Part VII — Combating Terrorism Financing
Money Laundering
Money laundering generally involves proceeds of unlawful offences or activities that are processed through transactions, concealments, or other means so that they appear to have originated from a legitimate source. There are three stages in money laundering and there may be numerous transactions that could alert a reporting institution to the money laundering activities as below. Reporting institution means a person carrying on regulated activities under the CMSA as specified under the First Schedule of the AMLA.
The following are the three stages of money laundering.
• Placement – The physical disposal of proceeds of unlawful offences or activities by introducing into the financial system, typically in the form of cash.
• Layering – The separation of proceeds of unlawful offences or activities from their source by creating layers of financial transactions designed to disguise the audit trail.
• Integration – Laundered proceeds re-enter the financial system and are integrated into the economy, so they appear the same as any legitimate funds.
Terrorism Financing
Financing of terrorism generally refers to carrying out transactions involving funds or property, whether from a legitimate or illegitimate source, that may or may not be owned by terrorists, or those have been, or are intended to be used to assist the commission of terrorist acts, and/or the financing of terrorist and terrorist organisations. Note that unlike money laundering, in the case of terrorism financing, the source of funds could be legitimate and from non-terrorist persons or organisations.
For more information, please refer to Guidelines on Prevention of Money Laundering and Terrorism Financing for Reporting Institutions in the Capital Market.
Summary
In this topic we considered how shares are traded on Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad using the automated trading system. We looked in detail at the various steps undertaken by Participating Organisations and dealer’s representatives in executing a client order and understood in further detail the operations of the Exchange in the Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad Participating Organisations’ Trading Manual.
We considered how the Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad regulate the way in which Participating Organisations conduct business. In particular, we looked at those rules which affect dealing in securities and trading by Participating Organisations. We also looked at the core principles of supervision used as guidance by the stockbroking companies and their representatives in the Guidelines on Market Conduct and Business Practices for Stockbroking Companies and Licensed Representatives to promote a culture of compliance, professionalism, ethics and responsibility. Finally, we took a brief look at Guidelines on Prevention of Money Laundering and Terrorism Financing for Reporting Institutions in the Capital Market.
Self-Assessment
1. What is the minimum retail commission payable in terms of % calculated for the contracts below?
Contract A —The contract value is RM80,000. Answer: 0.6%
Contract B —The contract value is RM128,000. Answer: 0.3%
2. “Y is an individual who has been entrusted domestically with prominent public functions, for example as Head of State or of government, senior politician, senior government, judicial or military official, senior executive of a state-owned corporation, important political party official.”
Which of the following persons is described in the above statement in relation to Guidelines on Prevention of Money Laundering and Terrorism Financing for Reporting Institutions in the Capital Market?
A. Legal Person
B. Special Officer
C. Beneficial Owner
D. Politically Exposed Person (PEP)
3. “This order remains in the order book if it is not fully matched, from the time it is entered till it reaches its specified expiry date, cancelled by the Participating Organisation or withdrawn by the Exchange. Unmatched quantities are carried forward to the following trading day.”
Which of the following order validity matches the description above?
A. Day Order
B. Fill-Or-Kill (FOK) order
c. Bursa Goof-Till-Date (Bursa FTD) order
D. Bursa Good-Till-Cancel (Bursa GTC) order
